当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Eur. Phys. J. D
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Structural evolution of free-standing 2D silicon carbide upon heating
The European Physical Journal D ( IF 1.5 ) Pub Date : 2020-06-09 , DOI: 10.1140/epjd/e2020-10101-1 Tue Minh Le Nguyen , Vo Van Hoang , Hang T. T. Nguyen
中文翻译:

独立式二维碳化硅在加热时的结构演变

The European Physical Journal D ( IF 1.5 ) Pub Date : 2020-06-09 , DOI: 10.1140/epjd/e2020-10101-1 Tue Minh Le Nguyen , Vo Van Hoang , Hang T. T. Nguyen
Abstract
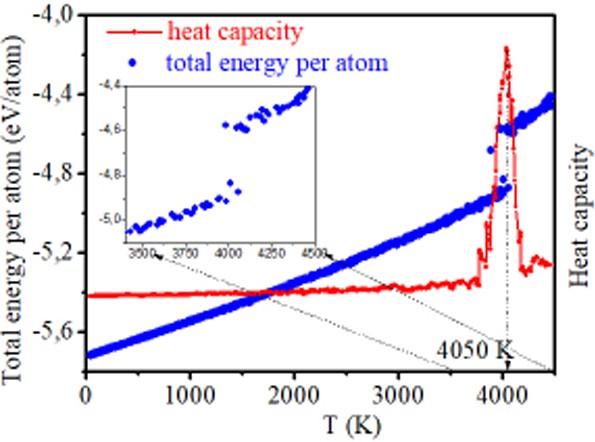
Two-dimensional Silicon Carbide (2D SiC) model is studied via molecular dynamics simulation to observe the structural evolution upon heating. A model contains 11040 atoms interacting via Vashishta potentials. The model is heated up from 50 K to 4500 K in order to observe the changes in structures during heating process. The melting point of free-standing 2D SiC is defined to be around 4050 K by temperature dependence of the heat capacity. The Lindemann criterion for 2D case is calculated and used to classify the behaviors of the liquid like and solid like atoms. The atomic mechanism of structural evolution upon heating is analyzed based on the occurrence/growth of liquid like atoms the average coordination number the ring statistics as well as the angular distributions.Graphical abstract

中文翻译:

独立式二维碳化硅在加热时的结构演变
摘要
通过分子动力学模拟研究了二维碳化硅(2D SiC)模型,以观察加热时的结构演变。一个模型包含11040个通过Vashishta电位相互作用的原子。将模型从50 K加热到4500 K,以观察加热过程中结构的变化。根据热容的温度依赖性,将独立式2D SiC的熔点定义为4050 K左右。计算二维情况下的Lindemann准则,并将其用于分类液体状和固体状原子的行为。基于液体状原子的出现/增长,平均配位数,环的统计以及角度分布,分析了加热时结构演化的原子机理。图形概要












































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号