Electrocatalysis ( IF 2.7 ) Pub Date : 2019-06-07 , DOI: 10.1007/s12678-019-00541-6 Kai Zhu , Xiaoli Ren , Xiuping Sun , Lijing Zhu , Zhirong Sun
This study presents a comparative investigation of supporting electrolyte effect on the surface corrosion and anodic oxidation performance of graphite electrode. The effect of electrolyte on the electrochemical behavior is investigated in solution containing 0.05 mol L−1 sodium salt, using current-overpotential curves and Tafel lines. The surface morphology and composition of the graphite anodes before and after electrolysis are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Raman spectra. In aqueous solution, graphite anode is positive polarized, functionalizes the surface, and releases soluble organics. The light-absorbing corrosion products of graphite anode are recorded by a UV-Vis spectrophotometer in the ultraviolet wavelength range. Batch experiments on atrazine oxidation show that NaCl is more efficient than Na2SO4 and NaNO3 to promote the combustion of organics due to the mediated oxidation of the electrogenerated active chlorine species. The oxidation process is confirmed to employ a non-radical mechanism in which the organics are degraded at the active sites of graphite anode.
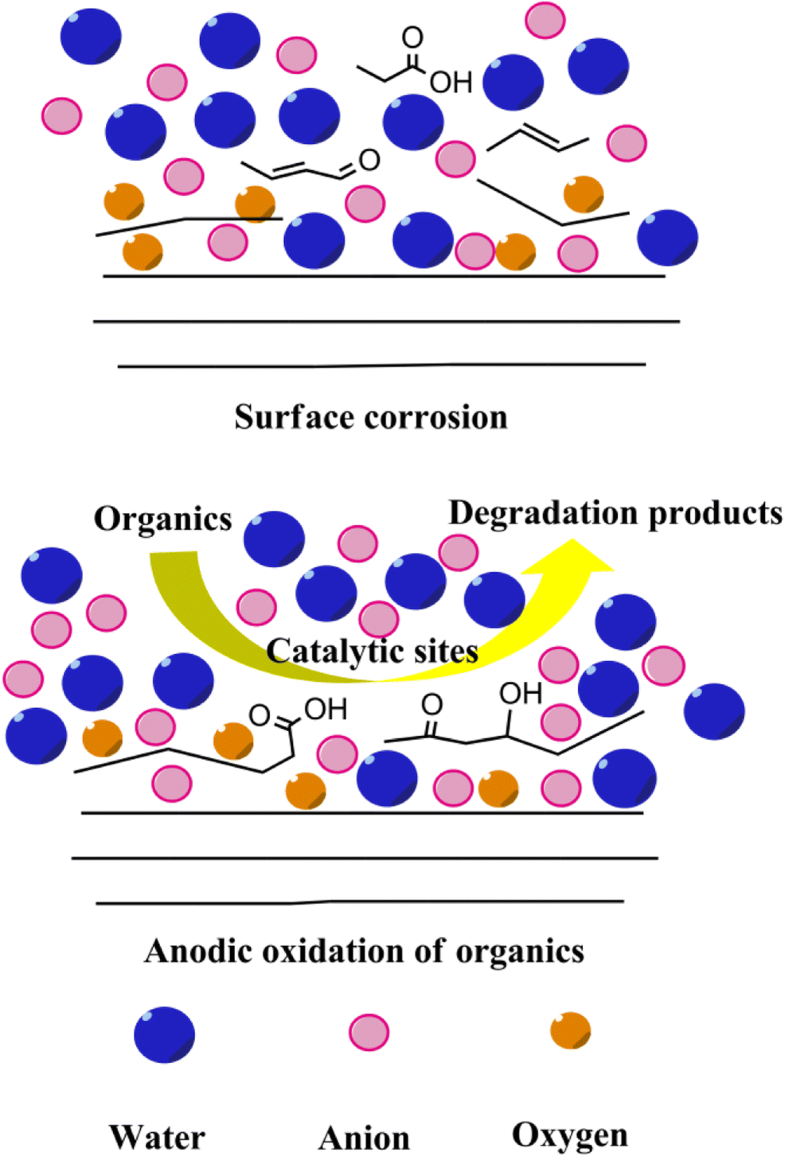
Carbon anodes have been widely employed for organics removal during anodic oxidation process, however, oxidation of contaminants with these materials is usually accompanied by electro-corrosion. This paper presents a comparative investigation of supporting electrolyte effect on the surface corrosion and anodic oxidation performance, using graphite felt as the example, to extend our knowledge of the mechanistic behavior of carbon anodes.
中文翻译:

支撑电解质对石墨电极表面腐蚀和阳极氧化性能的影响
这项研究提供了比较研究支持电解质对石墨电极的表面腐蚀和阳极氧化性能的影响。在含0.05 mol L -1的溶液中研究了电解质对电化学行为的影响钠盐,使用电流-超电势曲线和Tafel线。通过扫描电子显微镜,X射线衍射和拉曼光谱表征电解前后石墨阳极的表面形态和组成。在水溶液中,石墨阳极是正极化的,可对表面进行功能化并释放出可溶性有机物。用紫外可见分光光度计在紫外波长范围内记录石墨阳极的吸光腐蚀产物。at去津氧化的批量实验表明,NaCl比Na 2 SO 4和NaNO 3更有效由于电生成的活性氯物种的介导氧化,从而促进有机物的燃烧。证实该氧化过程采用非自由基机理,其中有机物在石墨阳极的活性位点处降解。

碳阳极已被广泛用于阳极氧化过程中的有机物去除,但是,这些材料对污染物的氧化通常伴随着电腐蚀。本文以石墨毡为例,对支持电解质对表面腐蚀和阳极氧化性能的影响进行了比较研究,以扩展我们对碳阳极力学行为的认识。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号