Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2019-01-24 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1544-2 Rohawi Nur Syakila , Siong Meng Lim , Snezana Agatonovic-Kustrin , Fei Tieng Lim , Kalavathy Ramasamy
The cholesterol-lowering properties of 12 lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in the absence or presence of 0.3% bile salts were assessed and compared quantitatively and qualitatively in vitro. A new, more sensitive and cost-effective high-performance thin-layer chromatography method combined with digital image evaluation of derivatised chromatographic plates was developed and validated to quantify cholesterol in LAB culture media. The performance of the method was compared with that of the o-phthalaldehyde method. For qualitative assessment, assimilated fluorescently tagged cholesterol was visualised by confocal microscopy. All LAB strains exhibited a cholesterol-lowering effect of various degrees (19–59% in the absence and 14–69% in the presence of bile salts). Lactobacillus plantarum LAB12 and Pentosaceus pentosaceus LAB6 were the two best strains of lactobacilli and pediococci. They lowered cholesterol levels by 59% and 54%, respectively, in the absence and by 69% and 58%, respectively, in the presence of bile salts. Confocal microscopy showed that cholesterol was localised at the outermost cell membranes of LAB12 and LAB6. The present findings warrant in-depth in vivo study.
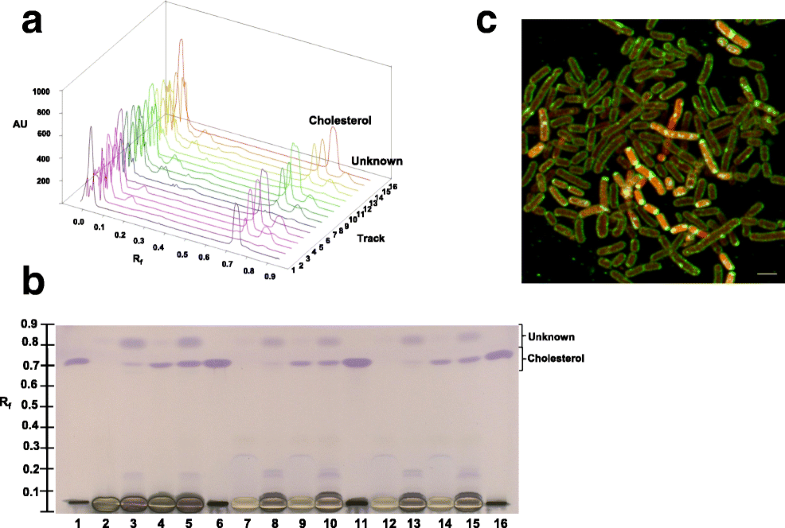
(A) 3D plots based on scan at 525 nm of (B) derivatized HPTLC plate of separated cholesterol and (C) confocal microscopic image showing the localisation of NBD-cholesterol assimilated by LAB
中文翻译:

使用数字增强型高效薄层色谱和共聚焦显微镜对小儿球菌和乳杆菌诱导的胆固醇降低作用进行体外评估
在不存在或存在0.3%胆汁盐的情况下,对12种乳酸菌(LAB)的降胆固醇性能进行了评估,并在体外进行了定量和定性的比较。开发了一种新的,更灵敏且具有成本效益的高性能薄层色谱方法,并结合了衍生化色谱板的数字图像评估,并经过验证可对LAB培养基中的胆固醇进行定量。将该方法的性能与邻苯二甲醛方法的性能进行了比较。为了进行定性评估,通过共聚焦显微镜观察了同化的荧光标记胆固醇。所有LAB菌株均表现出不同程度的胆固醇降低作用(在不存在胆汁盐的情况下降低19-59%,在存在胆盐的情况下降低14-69%)。植物乳杆菌LAB12和Pentosaceus pentosaceus LAB6是乳酸菌和小球菌的两种最佳菌株。在不存在胆汁盐的情况下,胆固醇水平分别降低了59%和54%,在存在胆盐的情况下分别降低了69%和58%。共聚焦显微镜显示胆固醇位于LAB12和LAB6的最外层细胞膜上。目前的发现值得深入的体内研究。

(A)基于525 nm扫描的3D图(B)分离的胆固醇的衍生化HPTLC板和(C)共聚焦显微镜图像,显示LAB吸收的NBD-胆固醇的定位











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号