当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Energy Environ. Sci.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Electrochemomechanics of lithium dendrite growth
Energy & Environmental Science ( IF 32.4 ) Pub Date : 2019-11-14 , DOI: 10.1039/c9ee01864f Aniruddha Jana 1, 2, 3, 4 , Sang Inn Woo 1, 2, 3, 4 , K. S. N. Vikrant 1, 2, 3, 4 , R. Edwin García 1, 2, 3, 4
Energy & Environmental Science ( IF 32.4 ) Pub Date : 2019-11-14 , DOI: 10.1039/c9ee01864f Aniruddha Jana 1, 2, 3, 4 , Sang Inn Woo 1, 2, 3, 4 , K. S. N. Vikrant 1, 2, 3, 4 , R. Edwin García 1, 2, 3, 4
Affiliation

|
A comprehensive roadmap describing the current density- and size-dependent dendrite growth mechanisms is presented. Based on a thermodynamically consistent theory, the combined effects of chemical diffusion, electrodeposition, and elastic and plastic deformation kinetics are analyzed to rationalize their contributions to experimentally observable morphologies. A critical current density, î* = z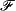 iliml(ΔGΩκi), in the tσ < t < tSand range, results in plastic flow at the tips, dendrite bifurcation, and bent and kinked morphologies. Three dendrite growth mechanisms are observed: (1) electrochemical shielding, where there is practically no electrodeposition/electrodissolution; (2) stress-induced electrodissolution and electrodeposition on those interfaces directly facing each other, generating a self-sustained overpotential that pushes the dendrites towards the counter electrode; and (3) local, lateral plastic extrusion in those side branches experiencing non-hydrostatic stresses. Six regimes of lithium electrodeposit growth are identified: (i) thermodynamic suppression regime, (ii) incubation regime, (iii) base-controlled regime, (iv) tip-controlled regime, (v) mixed regime, and (vi) Sand's regime.
iliml(ΔGΩκi), in the tσ < t < tSand range, results in plastic flow at the tips, dendrite bifurcation, and bent and kinked morphologies. Three dendrite growth mechanisms are observed: (1) electrochemical shielding, where there is practically no electrodeposition/electrodissolution; (2) stress-induced electrodissolution and electrodeposition on those interfaces directly facing each other, generating a self-sustained overpotential that pushes the dendrites towards the counter electrode; and (3) local, lateral plastic extrusion in those side branches experiencing non-hydrostatic stresses. Six regimes of lithium electrodeposit growth are identified: (i) thermodynamic suppression regime, (ii) incubation regime, (iii) base-controlled regime, (iv) tip-controlled regime, (v) mixed regime, and (vi) Sand's regime.
中文翻译:

锂枝晶生长的电化学机理
提出了描述当前密度和尺寸依赖性枝晶生长机制的综合路线图。基于热力学一致的理论,分析了化学扩散,电沉积以及弹性和塑性变形动力学的综合影响,以合理化它们对实验可观察形态的贡献。甲临界电流密度,î * = ž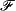 我LIM升(Δ GΩκ我),在吨σ <吨<吨砂范围,会导致尖端的塑性流动,枝晶分叉以及弯曲和扭结的形态。观察到三种枝晶生长机制:(1)电化学屏蔽,实际上没有电沉积/电溶解;(2)应力诱导的电溶解和在彼此直接面对的界面上的电沉积,产生自我维持的超电势,将树枝状晶体推向对电极;(3)在那些承受非静水压力的侧支中进行局部,横向塑性挤压。锂电沉积物生长的六种方式被确定:(i)热力学抑制方式,(ii)孵育方式,(iii)碱控制方式,(iv)尖端控制方式,(v)混合方式和(vi)沙氏方式。
我LIM升(Δ GΩκ我),在吨σ <吨<吨砂范围,会导致尖端的塑性流动,枝晶分叉以及弯曲和扭结的形态。观察到三种枝晶生长机制:(1)电化学屏蔽,实际上没有电沉积/电溶解;(2)应力诱导的电溶解和在彼此直接面对的界面上的电沉积,产生自我维持的超电势,将树枝状晶体推向对电极;(3)在那些承受非静水压力的侧支中进行局部,横向塑性挤压。锂电沉积物生长的六种方式被确定:(i)热力学抑制方式,(ii)孵育方式,(iii)碱控制方式,(iv)尖端控制方式,(v)混合方式和(vi)沙氏方式。
更新日期:2019-11-14
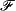 iliml(ΔGΩκi), in the tσ < t < tSand range, results in plastic flow at the tips, dendrite bifurcation, and bent and kinked morphologies. Three dendrite growth mechanisms are observed: (1) electrochemical shielding, where there is practically no electrodeposition/electrodissolution; (2) stress-induced electrodissolution and electrodeposition on those interfaces directly facing each other, generating a self-sustained overpotential that pushes the dendrites towards the counter electrode; and (3) local, lateral plastic extrusion in those side branches experiencing non-hydrostatic stresses. Six regimes of lithium electrodeposit growth are identified: (i) thermodynamic suppression regime, (ii) incubation regime, (iii) base-controlled regime, (iv) tip-controlled regime, (v) mixed regime, and (vi) Sand's regime.
iliml(ΔGΩκi), in the tσ < t < tSand range, results in plastic flow at the tips, dendrite bifurcation, and bent and kinked morphologies. Three dendrite growth mechanisms are observed: (1) electrochemical shielding, where there is practically no electrodeposition/electrodissolution; (2) stress-induced electrodissolution and electrodeposition on those interfaces directly facing each other, generating a self-sustained overpotential that pushes the dendrites towards the counter electrode; and (3) local, lateral plastic extrusion in those side branches experiencing non-hydrostatic stresses. Six regimes of lithium electrodeposit growth are identified: (i) thermodynamic suppression regime, (ii) incubation regime, (iii) base-controlled regime, (iv) tip-controlled regime, (v) mixed regime, and (vi) Sand's regime.
中文翻译:

锂枝晶生长的电化学机理
提出了描述当前密度和尺寸依赖性枝晶生长机制的综合路线图。基于热力学一致的理论,分析了化学扩散,电沉积以及弹性和塑性变形动力学的综合影响,以合理化它们对实验可观察形态的贡献。甲临界电流密度,î * = ž
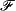 我LIM升(Δ GΩκ我),在吨σ <吨<吨砂范围,会导致尖端的塑性流动,枝晶分叉以及弯曲和扭结的形态。观察到三种枝晶生长机制:(1)电化学屏蔽,实际上没有电沉积/电溶解;(2)应力诱导的电溶解和在彼此直接面对的界面上的电沉积,产生自我维持的超电势,将树枝状晶体推向对电极;(3)在那些承受非静水压力的侧支中进行局部,横向塑性挤压。锂电沉积物生长的六种方式被确定:(i)热力学抑制方式,(ii)孵育方式,(iii)碱控制方式,(iv)尖端控制方式,(v)混合方式和(vi)沙氏方式。
我LIM升(Δ GΩκ我),在吨σ <吨<吨砂范围,会导致尖端的塑性流动,枝晶分叉以及弯曲和扭结的形态。观察到三种枝晶生长机制:(1)电化学屏蔽,实际上没有电沉积/电溶解;(2)应力诱导的电溶解和在彼此直接面对的界面上的电沉积,产生自我维持的超电势,将树枝状晶体推向对电极;(3)在那些承受非静水压力的侧支中进行局部,横向塑性挤压。锂电沉积物生长的六种方式被确定:(i)热力学抑制方式,(ii)孵育方式,(iii)碱控制方式,(iv)尖端控制方式,(v)混合方式和(vi)沙氏方式。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号