Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2019-02-13 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-01656-x Anna Laura Capriotti , Chiara Cavaliere , Susy Piovesana
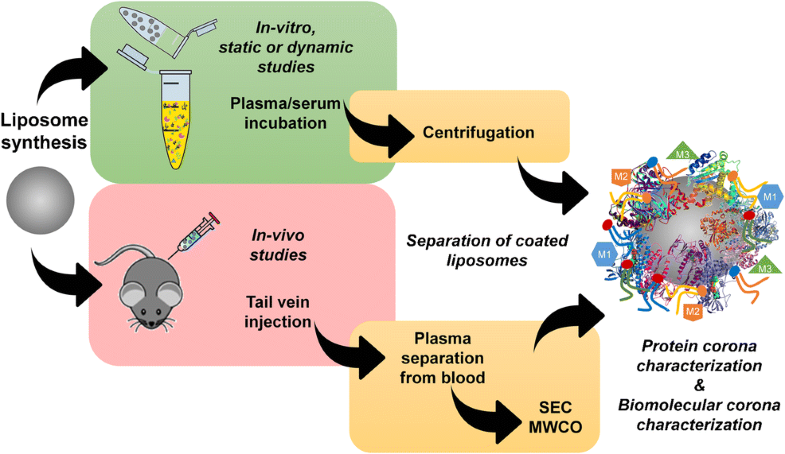
This trends article describes the analytical approaches for the in-depth characterization of the protein corona on liposome nanoparticles. In particular, examples since 2014 are summarized according to the analytical approach. Traditional protein corona characterizations from in vitro static experiments are provided along with the newly introduced experimental setups for characterization of the protein corona by in vitro dynamic and in vivo studies. Additionally, a special attention is also devoted to the need for introduction of new experimental workflows for characterization of a much wider array of biomolecules. In the most recent years, an extension of the protein corona concept to the biomolecular corona was introduced, and the analytical targets are no longer restricted to proteins, but to other important biomolecules as well, as they can potentially affect the biodistribution and interaction of nanoparticles with the biological systems. The few recent examples in this field are discussed for the characterization of metabolites and lipids in the biomolecular corona with examples, also extending the discussion from liposome to other types of nanoparticles. A final discussion is provided on the potential key role of the most recent omics approaches in the study of the nano-bio interface, with an overview on top-down proteomics, which allows a better elucidation of proteoforms, and on lipidomics and metabolomics, which allow a comprehensive untargeted characterization of lipids and metabolites, respectively.
Graphical abstract
中文翻译:

脂质体蛋白电晕表征是纳米医学中的一种新方法
这篇趋势文章描述了脂质体纳米颗粒上蛋白质电晕的深入表征的分析方法。特别是,根据分析方法总结了2014年以来的示例。提供了来自体外静态实验的传统蛋白质电晕表征,以及新近引入的用于通过体外动态和体内研究表征蛋白质电晕的实验装置。此外,还特别需要引入新的实验工作流程,以表征更广泛的生物分子。近年来,引入了蛋白质电晕概念到生物分子电晕的扩展,并且分析目标不再局限于蛋白质,而也限于其他重要的生物分子,因为它们可能会影响纳米颗粒的生物分布和与生物系统的相互作用。讨论了该领域的一些近期实例,以举例说明生物分子电晕中代谢物和脂质的表征,并将讨论范围从脂质体扩展到其他类型的纳米颗粒。最后讨论了最新的组学方法在纳米生物界面研究中的潜在关键作用,并概述了自上而下的蛋白质组学(可更好地阐明蛋白质形式)以及脂质组学和代谢组学,分别对脂质和代谢物进行全面的非靶向表征。讨论了该领域的一些近期实例,以举例说明生物分子电晕中代谢物和脂质的表征,并将讨论范围从脂质体扩展到其他类型的纳米颗粒。最后讨论了最新的组学方法在纳米生物界面研究中的潜在关键作用,并概述了自上而下的蛋白质组学(可更好地阐明蛋白质形式)以及脂质组学和代谢组学,分别对脂质和代谢物进行全面的非靶向表征。讨论了该领域的一些近期实例,以举例说明生物分子电晕中代谢物和脂质的表征,并将讨论范围从脂质体扩展到其他类型的纳米颗粒。最后讨论了最新的组学方法在纳米生物界面研究中的潜在关键作用,并概述了自上而下的蛋白质组学(可以更好地阐明蛋白形式)以及脂质组学和代谢组学,分别对脂质和代谢物进行全面的非靶向表征。

图形概要









































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号