Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2019-02-09 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-01626-3 Yunfei Hua , Xuping Yang , Ruiting Li , Peifang Liu , Peijia Liu , Linrui Li , Xia Yuan , Xiaoyi Hua , Yuan Tian , Zunjian Zhang , Yin Huang
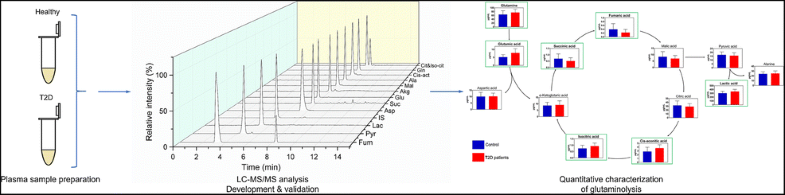
Glutaminolysis is the metabolic pathway that lyses glutamine to glutamate, alanine, citrate, aspartate, and so on. As partially recruiting reaction steps from the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and the malate-aspartate shuttle, glutaminolysis takes essential place in physiological and pathological situations. We herein developed a sensitive, rapid, and reproducible liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method to determine the perturbation of glutaminolysis in human plasma by quantifying 13 involved metabolites in a single 20-min run. A pHILIC column with a gradient elution system consisting of acetonitrile-5 mM ammonium acetate was used for separation, while an electrospray ionization source (ESI) operated in negative mode with multiple reaction monitoring was employed for detection. The method was fully validated according to FDA’s guidelines, and it generally provided good results in terms of linearity (the correlation coefficient no less than 0.9911 within the range of 0.05–800 μg/mL), intra- and inter-day precision (less than 18.38%) and accuracy (relative standard deviation between 89.24 and 113.4%), with lower limits of quantification between 0.05 and 10 μg/mL. The new analytical approach was successfully applied to analyze the plasma samples from 38 healthy volunteers and 34 patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Based on the great sensitivity and comprehensive capacity, the targeted analysis revealed the imperceptible abnormalities in the concentrations of key intermediates, such as iso-citrate and cis-aconitate, thus allowing us to obtain a thorough understanding of glutaminolysis disorder during T2D.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

液相色谱-串联质谱法定量分析人血浆中的谷氨酰胺分解
谷氨酰胺分解是将谷氨酰胺裂解为谷氨酸,丙氨酸,柠檬酸盐,天冬氨酸等的代谢途径。由于从三羧酸(TCA)循环和苹果酸-天冬氨酸穿梭中部分招募了反应步骤,因此在生理和病理情况下,谷氨酰胺分解必不可少。我们在本文中开发了一种灵敏,快速且可重现的液相色谱-串联质谱方法,通过在20分钟内对13种涉及的代谢物进行定量,从而确定人血浆中谷氨酰胺分解的扰动。一个p使用具有由乙腈-5 mM醋酸铵组成的梯度洗脱系统的HILIC色谱柱进行分离,同时采用负离子模式操作的电喷雾电离源(ESI)进行多反应监测。该方法已根据FDA指南进行了充分验证,并且在线性(相关系数在0.05–800μg/ mL范围内,相关系数不小于0.9911),日内和日间精度(小于18.38%)和准确度(相对标准偏差在89.24和113.4%之间),定量下限在0.05和10μg/ mL之间。新的分析方法已成功应用于分析38位健康志愿者和34位2型糖尿病(T2D)患者的血浆样本。基于高度的敏感性和综合能力,顺乌头酸,因此使我们能够全面了解T2D期间的谷氨酰胺分解障碍。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号