Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2019-02-09 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-01636-1 Carolina V. Uliana , Tássia R. de Oliveira , Márcia R. Cominetti , Ronaldo C. Faria
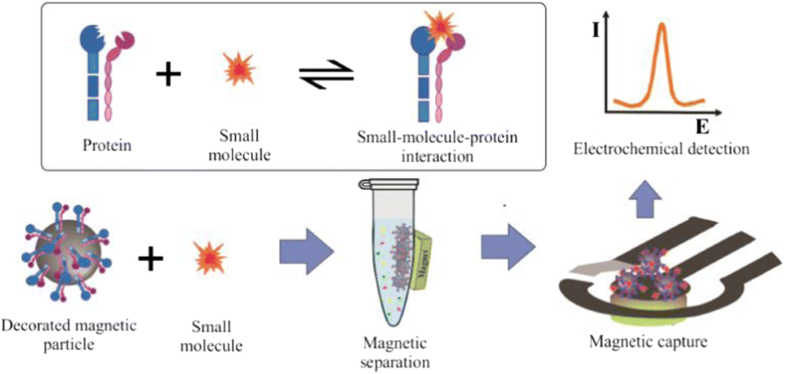
The evaluation of interaction between small molecules and protein is an important step in the discovery of new drugs and to study complex biological systems. In this work, an alternative method was presented to evaluate small-molecule–protein interaction by using ligand capture by protein-coated magnetic particles (MPs) and disposable electrochemical cells. The interaction study was conducted using [10]-gingerol from ginger rhizome and a transmembrane protein αVβ3 integrin. Initially, the electrochemical behavior of the natural compound [10]-gingerol was evaluated with the disposable carbon-based electrodes and presented an irreversible oxidation process controlled by diffusion. The analytical curve for [10]-gingerol was obtained in the range of 1.0 to 20.0 μmol L−1, with limit of detection of 0.26 μmol L−1. Then MPs coated with αVβ3 integrin were incubated with standard solutions and extracts of ginger rhizome for [10]-gingerol capture and separation. The bioconjugate obtained was dropped to the disposable electrochemical cells, keeping a permanent magnet behind the working electrode, and the binding process was evaluated by the electrochemical detection of [10]-gingerol. The assay method proposed was also employed to calculate the [10]-gingerol–αVβ3 integrin association constant, which was calculated as 4.3 × 107 M−1. The method proposed proved to be a good label-free alternative to ligand–protein interaction studies.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用磁捕获和电化学检测对小分子-蛋白质相互作用进行无标记评估
评估小分子与蛋白质之间的相互作用是发现新药和研究复杂生物系统的重要一步。在这项工作中,提出了一种替代方法,该方法通过使用被蛋白包裹的磁性粒子(MP)和一次性电化学电池捕获的配体来评估小分子与蛋白质的相互作用。使用姜根茎中的[10]-姜油醇和跨膜蛋白αVβ3整联蛋白进行了相互作用研究。最初,使用一次性碳基电极评估了天然化合物[10]-姜油的电化学行为,并提出了一种通过扩散控制的不可逆氧化过程。[1.0]-姜油酚的分析曲线在1.0至20.0μmolL -1的范围内获得,检出限为0.26μmolL-1。然后将涂有αVβ3整联蛋白的MP与标准溶液和生姜根茎提取物温育,以捕获和分离[10]-姜油。将获得的生物结合物滴入一次性电化学电池中,使永久磁铁保持在工作电极的后方,并通过电化学检测[10]-姜油醇评估结合过程。提出的测定方法也被用于计算[10]-姜油酸酯-αVβ3整联蛋白缔合常数,其计算为4.3×10 7 M -1。所提出的方法被证明是配体-蛋白质相互作用研究的一种很好的无标记替代方法。

ᅟ



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号