Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2019-02-01 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-01618-3 Eva Marguí , Jasna Jablan , Marko Gerić , Suzana Inić , Ana-Marija Domijan , Renato Janušić , Božena Šarčević , Ignasi Queralt , Verica Garaj-Vrhovac
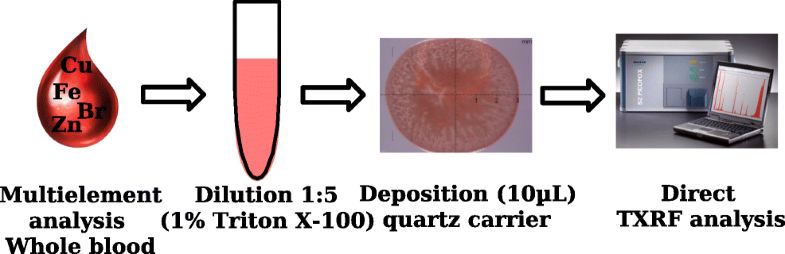
Multielemental analysis of whole blood can provide significant information for the evaluation of nutritional status and diagnosis of certain diseases as well as for the assessment of exposure to potentially toxic metals. However, the quantification of multiple elements in whole blood is not easy partly because of the wide variation in element concentrations (from ng L−1 to g L−1) and the complex matrix. The aim of this work was to develop a fast, sustainable, and reliable analytical method, in combination with low-power TXRF, for multielemental analysis of blood samples. Firstly, a set of experiments were carried out to select the best diluent type and dilution factor using the control material SeronormTM Trace Elements Whole Blood L-1. A critical evaluation of the parameters affecting the sample deposition on the reflector was also carried out including a study of the shape and element distribution of the deposited residue on the reflector by micro X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Using the best analytical conditions, limits of detection estimated were in the low milligrams per kilogram range and similar to those obtained using more complex sample treatments such as digestion. Accuracy and precision of the results were in most cases acceptable (recoveries 89–102%, RSD 6–8%, n = 5). Only underestimated values were obtained for light elements such as potassium. To prove the applicability of the method, several blood samples from control and thyroid disease patients were analyzed. Despite the fact that more samples need to be analyzed, it seems that Zn and Br contents in some of the patients are significantly higher compared to control samples.
Graphical abstract
中文翻译:

使用全反射X射线荧光光谱法对全血样品进行分析的严格评估:在甲状腺疾病患者中的应用
全血的多元素分析可为评估营养状况和诊断某些疾病以及评估暴露于潜在有毒金属提供重要信息。但是,全血中多种元素的定量分析并不容易,部分原因是元素浓度变化很大(从ng L -1到g L -1)和复数矩阵。这项工作的目的是开发一种与低功率TXRF结合的快速,可持续和可靠的分析方法,用于血液样品的多元素分析。首先,使用对照材料SeronormTM微量元素全血L-1进行了一组实验,以选择最佳的稀释剂类型和稀释倍数。还进行了影响样品在反射器上沉积的参数的关键评估,包括通过微X射线荧光光谱法研究反射器上沉积残留物的形状和元素分布。使用最佳分析条件,估计的检出限在每公斤低毫克范围内,与使用更复杂的样品处理(如消解)获得的检出限相似。n = 5)。对于轻元素(如钾)仅获得了低估的值。为了证明该方法的适用性,分析了一些来自对照和甲状腺疾病患者的血液样本。尽管需要分析更多的样品,但似乎某些患者中的Zn和Br含量明显高于对照样品。

图形概要



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号