Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin ( IF 1.5 ) Pub Date : 2021-08-01 , DOI: 10.1248/cpb.c21-00404 Takahiro Mori 1, 2, 3 , Kiyofumi Wanibuchi 1 , Hiroyuki Morita 4 , Ikuro Abe 1, 2
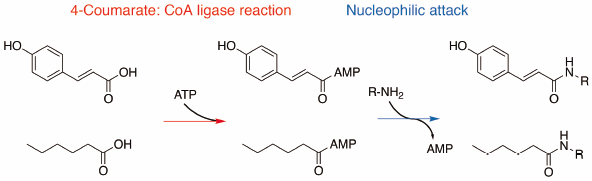
Amide bond formation is one of the most fundamental reactions in organic chemistry, and amide bonds constitute the key functional groups in natural products, peptides, and pharmaceuticals. Here we demonstrate the chemoenzymatic syntheses of 4-coumaroyl- and hexanoyl-amino acids, using 4-coumarate: CoA ligase from the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana (At4CL2). At4CL2 accepts 4-coumaric acid and hexanoic acid as the carboxylate substrates to generate acyl adenylates, which are captured by the amino group of amino acids to afford a series of N-acyl amides. This study shows the potential of 4CL for application as a biocatalyst to generate a series of biologically active amide compounds.
 Fullsize Image
Fullsize Image
中文翻译:

使用 4-香豆酸盐形成酰胺键:来自拟南芥的 CoA 连接酶
酰胺键的形成是有机化学中最基本的反应之一,酰胺键构成了天然产物、多肽和药物中的关键官能团。在这里,我们展示了使用 4-香豆酸:来自模式植物拟南芥(At4CL2) 的CoA 连接酶的 4-香豆酰和己酰氨基酸的化学酶促合成。At4CL2 接受 4-香豆酸和己酸作为羧酸盐底物以生成酰基腺苷酸,其被氨基酸的氨基捕获以提供一系列N-酰基酰胺。这项研究显示了 4CL 作为生物催化剂的应用潜力,可以产生一系列具有生物活性的酰胺化合物。
 全尺寸图像
全尺寸图像











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号