当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
The fate of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in a marine food web influenced by land-based sources in the Norwegian Arctic
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2021-3-11 , DOI: 10.1039/d0em00510j Aasim M. Ali 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Håkon A. Langberg 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 , Sarah E. Hale 4, 6, 7, 8 , Roland Kallenborn 4, 5, 10, 11, 12 , William F. Hartz 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 , Åse-Karen Mortensen 4, 9, 18, 19 , Tomasz Maciej Ciesielski 4, 9, 18, 19 , Carrie A. McDonough 20, 21, 22 , Bjørn Munro Jenssen 4, 9, 18, 19, 23 , Gijs D. Breedveld 4, 6, 7, 8, 24
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2021-3-11 , DOI: 10.1039/d0em00510j Aasim M. Ali 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Håkon A. Langberg 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 , Sarah E. Hale 4, 6, 7, 8 , Roland Kallenborn 4, 5, 10, 11, 12 , William F. Hartz 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 , Åse-Karen Mortensen 4, 9, 18, 19 , Tomasz Maciej Ciesielski 4, 9, 18, 19 , Carrie A. McDonough 20, 21, 22 , Bjørn Munro Jenssen 4, 9, 18, 19, 23 , Gijs D. Breedveld 4, 6, 7, 8, 24
Affiliation

|
Although poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) are ubiquitous in the Arctic, their sources and fate in Arctic marine environments remain unclear. Herein, abiotic media (water, snow, and sediment) and biotic media (plankton, benthic organisms, fish, crab, and glaucous gull) were sampled to study PFAS uptake and fate in the marine food web of an Arctic Fjord in the vicinity of Longyearbyen (Svalbard, Norwegian Arctic). Samples were collected from locations impacted by a firefighting training site (FFTS) and a landfill as well as from a reference site. Mean 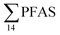 concentration in the landfill leachate was 643 ± 84 ng L−1, while it was 365 ± 8.0 ng L−1 in a freshwater pond and 57 ± 4.0 ng L−1 in a creek in the vicinity of the FFTS. These levels were an order of magnitude higher than in coastal seawater of the nearby fjord (maximum level
concentration in the landfill leachate was 643 ± 84 ng L−1, while it was 365 ± 8.0 ng L−1 in a freshwater pond and 57 ± 4.0 ng L−1 in a creek in the vicinity of the FFTS. These levels were an order of magnitude higher than in coastal seawater of the nearby fjord (maximum level 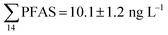 , at the FFTS impacted site). PFOS was the most predominant compound in all seawater samples and in freshly fallen snow (63–93% of
, at the FFTS impacted site). PFOS was the most predominant compound in all seawater samples and in freshly fallen snow (63–93% of  ). In freshwater samples from the Longyear river and the reference site, PFCA ≤ C9 were the predominant PFAS (37–59%), indicating that both local point sources and diffuse sources contributed to the exposure of the marine food web in the fjord.
). In freshwater samples from the Longyear river and the reference site, PFCA ≤ C9 were the predominant PFAS (37–59%), indicating that both local point sources and diffuse sources contributed to the exposure of the marine food web in the fjord. 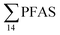 concentrations increased from zooplankton (1.1 ± 0.32 μg kg−1 ww) to polychaete (2.8 ± 0.80 μg kg−1 ww), crab (2.9 ± 0.70 μg kg−1 ww whole-body), fish liver (5.4 ± 0.87 μg kg−1 ww), and gull liver (62.2 ± 11.2 μg kg−1). PFAS profiles changed with increasing trophic level from a large contribution of 6:2 FTS, FOSA and long-chained PFCA in zooplankton and polychaetes to being dominated by linear PFOS in fish and gull liver. The PFOS isomer profile (branched versus linear) in the active FFTS and landfill was similar to historical ECF PFOS. A similar isomer profile was observed in seawater, indicating major contribution from local sources. However, a PFOS isomer profile enriched by the linear isomer was observed in other media (sediment and biota). Substitutes for PFOS, namely 6:2 FTS and PFBS, showed bioaccumulation potential in marine invertebrates. However, these compounds were not found in organisms at higher trophic levels.
concentrations increased from zooplankton (1.1 ± 0.32 μg kg−1 ww) to polychaete (2.8 ± 0.80 μg kg−1 ww), crab (2.9 ± 0.70 μg kg−1 ww whole-body), fish liver (5.4 ± 0.87 μg kg−1 ww), and gull liver (62.2 ± 11.2 μg kg−1). PFAS profiles changed with increasing trophic level from a large contribution of 6:2 FTS, FOSA and long-chained PFCA in zooplankton and polychaetes to being dominated by linear PFOS in fish and gull liver. The PFOS isomer profile (branched versus linear) in the active FFTS and landfill was similar to historical ECF PFOS. A similar isomer profile was observed in seawater, indicating major contribution from local sources. However, a PFOS isomer profile enriched by the linear isomer was observed in other media (sediment and biota). Substitutes for PFOS, namely 6:2 FTS and PFBS, showed bioaccumulation potential in marine invertebrates. However, these compounds were not found in organisms at higher trophic levels.
中文翻译:

受挪威北极土地来源影响的海洋食物网中多氟烷基物质和全氟烷基物质的命运
尽管北极地区普遍存在多氟烷基和全氟烷基物质(PFAS),但在北极海洋环境中其来源和命运仍不清楚。在此,对非生物介质(水,雪和沉积物)和生物介质(浮游生物,底栖生物,鱼类,螃蟹和白垩纪鸥)进行采样,以研究北极峡湾附近海洋食物网中PFAS的吸收和命运。朗伊尔城(挪威北极斯瓦尔巴特群岛)。从受消防训练场(FFTS)和垃圾填埋场影响的地方以及从参考点收集样品。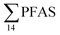 垃圾渗滤液中的平均浓度为643±84 ng L -1,而在淡水池塘中的平均浓度为365±8.0 ng L -1,而57±4.0 ng L -1在FFTS附近的一条小溪中 这些水位比附近峡湾的沿海海水高一个数量级
垃圾渗滤液中的平均浓度为643±84 ng L -1,而在淡水池塘中的平均浓度为365±8.0 ng L -1,而57±4.0 ng L -1在FFTS附近的一条小溪中 这些水位比附近峡湾的沿海海水高一个数量级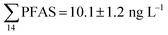 (在受FFTS影响的地点,最高水位)。全氟辛烷磺酸是所有海水样品和新鲜落雪中最主要的化合物(占63-93%
(在受FFTS影响的地点,最高水位)。全氟辛烷磺酸是所有海水样品和新鲜落雪中最主要的化合物(占63-93% )。在朗伊尔河和参考点的淡水样品中,PFCA≤C 9是主要的PFAS(37–59%),表明本地点源和散布源均导致了海湾中海洋食物网的暴露。
)。在朗伊尔河和参考点的淡水样品中,PFCA≤C 9是主要的PFAS(37–59%),表明本地点源和散布源均导致了海湾中海洋食物网的暴露。 从浮游动物(1.1±0.32μgkg -1 ww)到多毛(2.8±0.80μgkg -1 ww),螃蟹(2.9±0.70μgkg -1 ww全身),鱼肝(5.4±0.87μgkg-1 ww)和鸥肝(62.2±11.2μgkg -1)。PFAS的分布随营养水平的增加而变化,从浮游动物和多毛鱼类中的6:2 FTS,FOSA和长链PFCA的大量贡献变为以鱼和鸥肝中的线性PFOS为主。主动FFTS和垃圾填埋场中的PFOS异构体分布(分支与线性)类似于历史ECF PFOS。在海水中观察到类似的异构体分布,表明当地来源的主要贡献。但是,在其他介质(沉积物和生物群)中观察到了由线性异构体富集的PFOS异构体分布图。全氟辛烷磺酸替代品,即6:2 FTS和PFBS,在海洋无脊椎动物中显示出生物蓄积潜力。但是,在营养水平较高的生物体中未发现这些化合物。
从浮游动物(1.1±0.32μgkg -1 ww)到多毛(2.8±0.80μgkg -1 ww),螃蟹(2.9±0.70μgkg -1 ww全身),鱼肝(5.4±0.87μgkg-1 ww)和鸥肝(62.2±11.2μgkg -1)。PFAS的分布随营养水平的增加而变化,从浮游动物和多毛鱼类中的6:2 FTS,FOSA和长链PFCA的大量贡献变为以鱼和鸥肝中的线性PFOS为主。主动FFTS和垃圾填埋场中的PFOS异构体分布(分支与线性)类似于历史ECF PFOS。在海水中观察到类似的异构体分布,表明当地来源的主要贡献。但是,在其他介质(沉积物和生物群)中观察到了由线性异构体富集的PFOS异构体分布图。全氟辛烷磺酸替代品,即6:2 FTS和PFBS,在海洋无脊椎动物中显示出生物蓄积潜力。但是,在营养水平较高的生物体中未发现这些化合物。
更新日期:2021-03-11
 concentration in the landfill leachate was 643 ± 84 ng L−1, while it was 365 ± 8.0 ng L−1 in a freshwater pond and 57 ± 4.0 ng L−1 in a creek in the vicinity of the FFTS. These levels were an order of magnitude higher than in coastal seawater of the nearby fjord (maximum level
concentration in the landfill leachate was 643 ± 84 ng L−1, while it was 365 ± 8.0 ng L−1 in a freshwater pond and 57 ± 4.0 ng L−1 in a creek in the vicinity of the FFTS. These levels were an order of magnitude higher than in coastal seawater of the nearby fjord (maximum level 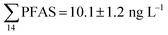 , at the FFTS impacted site). PFOS was the most predominant compound in all seawater samples and in freshly fallen snow (63–93% of
, at the FFTS impacted site). PFOS was the most predominant compound in all seawater samples and in freshly fallen snow (63–93% of  ). In freshwater samples from the Longyear river and the reference site, PFCA ≤ C9 were the predominant PFAS (37–59%), indicating that both local point sources and diffuse sources contributed to the exposure of the marine food web in the fjord.
). In freshwater samples from the Longyear river and the reference site, PFCA ≤ C9 were the predominant PFAS (37–59%), indicating that both local point sources and diffuse sources contributed to the exposure of the marine food web in the fjord. 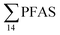 concentrations increased from zooplankton (1.1 ± 0.32 μg kg−1 ww) to polychaete (2.8 ± 0.80 μg kg−1 ww), crab (2.9 ± 0.70 μg kg−1 ww whole-body), fish liver (5.4 ± 0.87 μg kg−1 ww), and gull liver (62.2 ± 11.2 μg kg−1). PFAS profiles changed with increasing trophic level from a large contribution of 6:2 FTS, FOSA and long-chained PFCA in zooplankton and polychaetes to being dominated by linear PFOS in fish and gull liver. The PFOS isomer profile (branched versus linear) in the active FFTS and landfill was similar to historical ECF PFOS. A similar isomer profile was observed in seawater, indicating major contribution from local sources. However, a PFOS isomer profile enriched by the linear isomer was observed in other media (sediment and biota). Substitutes for PFOS, namely 6:2 FTS and PFBS, showed bioaccumulation potential in marine invertebrates. However, these compounds were not found in organisms at higher trophic levels.
concentrations increased from zooplankton (1.1 ± 0.32 μg kg−1 ww) to polychaete (2.8 ± 0.80 μg kg−1 ww), crab (2.9 ± 0.70 μg kg−1 ww whole-body), fish liver (5.4 ± 0.87 μg kg−1 ww), and gull liver (62.2 ± 11.2 μg kg−1). PFAS profiles changed with increasing trophic level from a large contribution of 6:2 FTS, FOSA and long-chained PFCA in zooplankton and polychaetes to being dominated by linear PFOS in fish and gull liver. The PFOS isomer profile (branched versus linear) in the active FFTS and landfill was similar to historical ECF PFOS. A similar isomer profile was observed in seawater, indicating major contribution from local sources. However, a PFOS isomer profile enriched by the linear isomer was observed in other media (sediment and biota). Substitutes for PFOS, namely 6:2 FTS and PFBS, showed bioaccumulation potential in marine invertebrates. However, these compounds were not found in organisms at higher trophic levels.
中文翻译:

受挪威北极土地来源影响的海洋食物网中多氟烷基物质和全氟烷基物质的命运
尽管北极地区普遍存在多氟烷基和全氟烷基物质(PFAS),但在北极海洋环境中其来源和命运仍不清楚。在此,对非生物介质(水,雪和沉积物)和生物介质(浮游生物,底栖生物,鱼类,螃蟹和白垩纪鸥)进行采样,以研究北极峡湾附近海洋食物网中PFAS的吸收和命运。朗伊尔城(挪威北极斯瓦尔巴特群岛)。从受消防训练场(FFTS)和垃圾填埋场影响的地方以及从参考点收集样品。
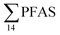 垃圾渗滤液中的平均浓度为643±84 ng L -1,而在淡水池塘中的平均浓度为365±8.0 ng L -1,而57±4.0 ng L -1在FFTS附近的一条小溪中 这些水位比附近峡湾的沿海海水高一个数量级
垃圾渗滤液中的平均浓度为643±84 ng L -1,而在淡水池塘中的平均浓度为365±8.0 ng L -1,而57±4.0 ng L -1在FFTS附近的一条小溪中 这些水位比附近峡湾的沿海海水高一个数量级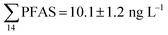 (在受FFTS影响的地点,最高水位)。全氟辛烷磺酸是所有海水样品和新鲜落雪中最主要的化合物(占63-93%
(在受FFTS影响的地点,最高水位)。全氟辛烷磺酸是所有海水样品和新鲜落雪中最主要的化合物(占63-93% )。在朗伊尔河和参考点的淡水样品中,PFCA≤C 9是主要的PFAS(37–59%),表明本地点源和散布源均导致了海湾中海洋食物网的暴露。
)。在朗伊尔河和参考点的淡水样品中,PFCA≤C 9是主要的PFAS(37–59%),表明本地点源和散布源均导致了海湾中海洋食物网的暴露。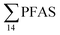 从浮游动物(1.1±0.32μgkg -1 ww)到多毛(2.8±0.80μgkg -1 ww),螃蟹(2.9±0.70μgkg -1 ww全身),鱼肝(5.4±0.87μgkg-1 ww)和鸥肝(62.2±11.2μgkg -1)。PFAS的分布随营养水平的增加而变化,从浮游动物和多毛鱼类中的6:2 FTS,FOSA和长链PFCA的大量贡献变为以鱼和鸥肝中的线性PFOS为主。主动FFTS和垃圾填埋场中的PFOS异构体分布(分支与线性)类似于历史ECF PFOS。在海水中观察到类似的异构体分布,表明当地来源的主要贡献。但是,在其他介质(沉积物和生物群)中观察到了由线性异构体富集的PFOS异构体分布图。全氟辛烷磺酸替代品,即6:2 FTS和PFBS,在海洋无脊椎动物中显示出生物蓄积潜力。但是,在营养水平较高的生物体中未发现这些化合物。
从浮游动物(1.1±0.32μgkg -1 ww)到多毛(2.8±0.80μgkg -1 ww),螃蟹(2.9±0.70μgkg -1 ww全身),鱼肝(5.4±0.87μgkg-1 ww)和鸥肝(62.2±11.2μgkg -1)。PFAS的分布随营养水平的增加而变化,从浮游动物和多毛鱼类中的6:2 FTS,FOSA和长链PFCA的大量贡献变为以鱼和鸥肝中的线性PFOS为主。主动FFTS和垃圾填埋场中的PFOS异构体分布(分支与线性)类似于历史ECF PFOS。在海水中观察到类似的异构体分布,表明当地来源的主要贡献。但是,在其他介质(沉积物和生物群)中观察到了由线性异构体富集的PFOS异构体分布图。全氟辛烷磺酸替代品,即6:2 FTS和PFBS,在海洋无脊椎动物中显示出生物蓄积潜力。但是,在营养水平较高的生物体中未发现这些化合物。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号