ISIJ International ( IF 1.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-08-18 , DOI: 10.2355/isijinternational.isijint-2019-749 Katsuya Hoshino 1, 2 , Katsunari Oikawa 2 , Wataru Tanimoto 3 , Masayasu Nagoshi 4 , Masaki Koba 1
It is known that the Al added to the Zn coating layer of hot-dip galvanized steel sheets (HDG) segregates on the surface of temper-rolled HDG as Al-based oxides with increasing aging time in air at room temperature. In this study, the surfaces of Zn-0.2mass%Al HDG with and without temper rolling were investigated to clarify the segregation mechanism. Specimens with a Zn coating weight of 55–57 g/m2 including 0.19–0.20 mass% of Al were used. The specimens were aged in air at 20°C or held in liquid nitrogen, and the surface and cross sections of the specimens were then observed and analyzed by XRF, SEM-EDX and EBSD. As a result, it was found that the velocity of Al-based oxide segregation on the surface of the temper-rolled HDG was much higher than that of the HDG without temper rolling. This was attributed to the difference in the area where formation of Al-based oxides was possible. It was also found that the Zn crystal grains in the coating layer were refined by recrystallization due to contact with the temper roll, resulting in an increased number of grain boundaries that can serve as Al diffusion paths. Some unrecrystallized grains also remained after temper rolling and could increase the number of formation sites for Al-based oxides, as they contain numerous dislocations that can serve as Al diffusion paths. These two different formation sites could lead to difference in the segregation rates observed in this study.
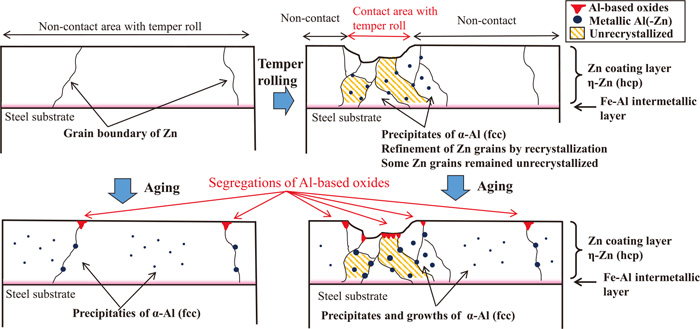 Schematic models of segregation of Al-based oxides on surface of HDG. Fullsize Image
Schematic models of segregation of Al-based oxides on surface of HDG. Fullsize Image
中文翻译:

Zn-0.2质量%Al热浸镀锌钢板表面Al基氧化物的偏析机理
众所周知,随着室温下空气中老化时间的增加,添加到热浸镀锌钢板(HDG)的Zn涂层中的Al以Al基氧化物的形式偏析在回火轧制HDG的表面上。在这项研究中,对Zn-0.2质量%Al HDG的表面进行了有无回火轧制的研究,以阐明其偏析机理。锌涂层重量为55–57 g / m 2的样品包括0.19–0.20质量%的Al。将样品在20°C的空气中老化或保持在液氮中,然后通过XRF,SEM-EDX和EBSD观察并分析样品的表面和横截面。结果,发现在回火轧制的HDG的表面上基于Al的氧化物的偏析速度远高于未回火轧制的HDG的速度。这归因于可能形成Al基氧化物的区域的差异。还发现由于与回火辊接触,涂层中的Zn晶粒通过重结晶而被细化,导致可以用作Al扩散路径的晶界数目增加。回火轧制后还会残留一些未结晶的晶粒,这些晶粒可能会增加Al基氧化物的形成部位数量,因为它们包含许多可以作为Al扩散路径的位错。这两个不同的形成位点可能导致本研究中观察到的偏析率不同。
 HDG表面Al基氧化物的偏析示意图。全尺寸图片
HDG表面Al基氧化物的偏析示意图。全尺寸图片











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号