Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin ( IF 1.7 ) Pub Date : 2020-08-01 , DOI: 10.1248/cpb.c20-00294 Satoru Tamura 1, 2 , Akihito Miyoshi 2 , Tomikazu Kawano 1 , Toshihiro Horii 3 , Sawako Itagaki 3 , Nobutoshi Murakami 2
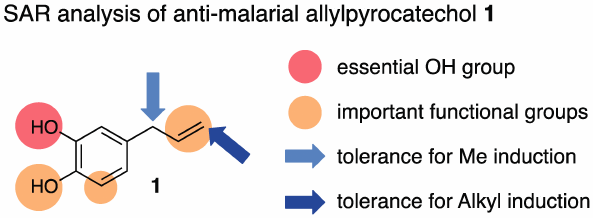
Malaria disease remains a serious worldwide health problem. In South-East Asia, one of the malaria infection “hot-spots,” medicinal plants such as Piper betle have traditionally been used for the treatment of malaria, and allylpyrocatechol (1), a constituent of P. betle, has been shown to exhibit anti-malarial activities. In this study, we verified that 1 showed in vivo anti-malarial activity through not only intraperitoneal (i.p.) but also peroral (p.o.) administration. Additionally, some analogs of 1 were synthesized and the structure–activity relationship was analyzed to disclose the crucial sub-structures for the potent activity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image
中文翻译:

从吹牛中分离得到的抗疟烯丙基邻苯二酚的构效关系。
疟疾仍然是世界范围内严重的健康问题。在东南亚,疟疾感染的一种“热点”的药用植物如荜betle传统上一直用于治疗疟疾,和allylpyrocatechol(1),的构成P. betle,已显示展示抗疟疾活动。在这项研究中,我们验证了1不仅通过腹膜内(ip )施用,而且还通过口服(po)施用表现出体内抗疟疾活性。此外,某些类似物1 合成并分析了结构-活性关系,以揭示有效活性的关键子结构。
 图形抽象全图
图形抽象全图



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号