当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
J. Fluoresc.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Detecting Mercury (II) and Thiocyanate Using "Turn-on" Fluorescence of Graphene Quantum Dots.
Journal of Fluorescence ( IF 2.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-07-20 , DOI: 10.1007/s10895-020-02586-z Faezeh Askari 1 , Abbas Rahdar 1 , Mohadeseh Dashti 2 , John F Trant 2
Journal of Fluorescence ( IF 2.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-07-20 , DOI: 10.1007/s10895-020-02586-z Faezeh Askari 1 , Abbas Rahdar 1 , Mohadeseh Dashti 2 , John F Trant 2
Affiliation
|
|
In this work, 1.8 nm graphene quantum dots (GQDs), exhibiting bright blue fluorescence, were prepared using a bottom-up synthesis from citric acid. The fluorescence of the GQDs could be almost completely quenched (about 96%) by adding Hg2+. Quenching was far less efficient with other similar heavy metals, Tl+, Pb2+ and Bi3+. Fluorescence could be near quantitatively restored through the introduction of thiocyanate. This “turn-on” fluorescence can thus be used to detect both or either environmental and physiological contaminants mercury and thiocyanate and could prove useful for the development of simple point-of-care diagnostics in the future.
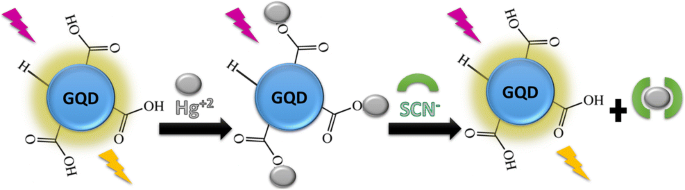 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
中文翻译:

使用石墨烯量子点的“开启”荧光检测汞 (II) 和硫氰酸盐。
在这项工作中,1.8 nm 石墨烯量子点 (GQD) 呈现出明亮的蓝色荧光,使用柠檬酸自下而上的合成方法制备。通过添加 Hg 2+几乎可以完全淬灭 GQD 的荧光(约 96%)。其他类似的重金属 Tl +、Pb 2+和 Bi 3+的淬火效率要低得多。通过引入硫氰酸盐可以近乎定量地恢复荧光。因此,这种“开启”荧光可用于检测环境和生理污染物汞和硫氰酸盐,或可用于检测环境和生理污染物汞和硫氰酸盐,并可证明对未来简单的床旁诊断的发展很有用。 图形概要
图形概要
更新日期:2020-07-20
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract中文翻译:

使用石墨烯量子点的“开启”荧光检测汞 (II) 和硫氰酸盐。
在这项工作中,1.8 nm 石墨烯量子点 (GQD) 呈现出明亮的蓝色荧光,使用柠檬酸自下而上的合成方法制备。通过添加 Hg 2+几乎可以完全淬灭 GQD 的荧光(约 96%)。其他类似的重金属 Tl +、Pb 2+和 Bi 3+的淬火效率要低得多。通过引入硫氰酸盐可以近乎定量地恢复荧光。因此,这种“开启”荧光可用于检测环境和生理污染物汞和硫氰酸盐,或可用于检测环境和生理污染物汞和硫氰酸盐,并可证明对未来简单的床旁诊断的发展很有用。
 图形概要
图形概要










































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号