当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Environ. Monit. Assess.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Spatio-temporal variation of air pollutants around the coal mining areas of Jharia Coalfield, India.
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment ( IF 2.9 ) Pub Date : 2020-05-30 , DOI: 10.1007/s10661-020-08324-z Shilpi Mondal 1 , Gurdeep Singh 1 , Manish Kumar Jain 1
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment ( IF 2.9 ) Pub Date : 2020-05-30 , DOI: 10.1007/s10661-020-08324-z Shilpi Mondal 1 , Gurdeep Singh 1 , Manish Kumar Jain 1
Affiliation
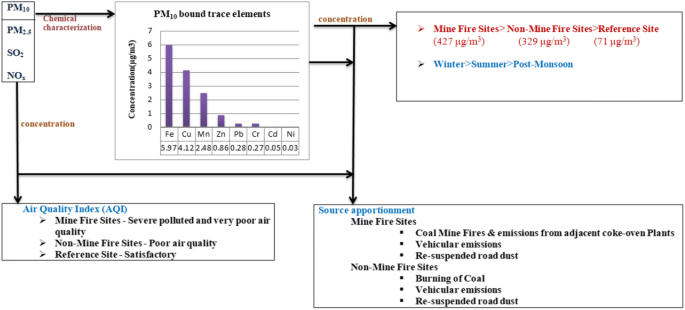
Jharia Coalfield (JCF) is one of the oldest coalfields in the eastern part of India and falls under critically polluted areas as per CPCB/MoEFCC Notification. Therefore, a study of air pollution and its management is the demand of the day. This study had been undertaken to know the current status of JCF concerning air quality. Ambient air quality monitoring with reference to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), SO2, NOx and trace elements had been conducted in the coal mining areas of JCF. The study area was divided into two groups, mainly fire and non-fire for the sampling of air. Principal component analysis (PCA) identified coal mine fire as a major source of air pollution in the mining areas of JCF. Air quality index (AQI) was calculated which revealed that the air quality index of coal mine fire-affected areas was nearly 1.5 times higher than that of the non-mine fire areas.
 Graphical abstract
Graphical abstract
中文翻译:

印度Jharia Coalfield煤矿区周围空气污染物的时空变化。
Jharia Coalfield(JCF)是印度东部最古老的煤田之一,并且根据CPCB / MoEFCC通知属于严重污染区域。因此,对空气污染及其管理的研究已成为当今的需求。进行这项研究是为了了解JCF在空气质量方面的现状。参照颗粒物(PM 10和PM 2.5),SO 2,NO x监测环境空气质量在JCF的煤矿区进行了微量元素测定。研究区域分为两类,主要是火灾采样和不火灾采样。主成分分析(PCA)将煤矿火灾确定为JCF矿区的主要空气污染源。计算得出的空气质量指数(AQI)表明,煤矿火灾影响地区的空气质量指数比非煤矿火灾地区高出近1.5倍。 图形概要
图形概要
更新日期:2020-05-30
 Graphical abstract
Graphical abstract中文翻译:

印度Jharia Coalfield煤矿区周围空气污染物的时空变化。
Jharia Coalfield(JCF)是印度东部最古老的煤田之一,并且根据CPCB / MoEFCC通知属于严重污染区域。因此,对空气污染及其管理的研究已成为当今的需求。进行这项研究是为了了解JCF在空气质量方面的现状。参照颗粒物(PM 10和PM 2.5),SO 2,NO x监测环境空气质量在JCF的煤矿区进行了微量元素测定。研究区域分为两类,主要是火灾采样和不火灾采样。主成分分析(PCA)将煤矿火灾确定为JCF矿区的主要空气污染源。计算得出的空气质量指数(AQI)表明,煤矿火灾影响地区的空气质量指数比非煤矿火灾地区高出近1.5倍。
 图形概要
图形概要










































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号