当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
CrystEngComm
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
A new Fourier transformation method for SAXS of polymer lamellar crystals
CrystEngComm ( IF 2.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-03-31 , DOI: 10.1039/d0ce00157k Xiangyang Li 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Jianjun Ding 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Pujing Chen 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Kang Zheng 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Lin Chen 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Xingyou Tian 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
CrystEngComm ( IF 2.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-03-31 , DOI: 10.1039/d0ce00157k Xiangyang Li 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Jianjun Ding 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Pujing Chen 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Kang Zheng 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Lin Chen 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Xingyou Tian 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Affiliation

|
For a long time, the scattering of semi-crystalline polymers was assumed to be from the electron density correlation in a lamellar stack. The Fourier transform for scattering can help obtain the correlation function and interface distribution function (IDF), from which the structural information can be obtained. Recently, we found that the scattering of the interface electrons involved in an evanescent wave (Iiev) is the actual origin (Li et al., IUCrJ, 2019, 6, 968–983). It is necessary to develop a new Fourier transform method to obtain structural information. In this study, a method similar to the classical method was proposed; nevertheless, the aim of multiplying q2 or q4 is to reduce the influence of the form factor, while the scattering in Fourier transform should be Iiev, which is roughly equal to the increased scattering during crystallization. The functions obtained by the Fourier transforms Kev and 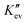 are similar to the correlation function and IDF in shape, respectively. Nevertheless, both of them are determined mainly by three items, i.e., the self-interference term of the first interface F11, the interference term between the first and second interfaces F12, and the interference term between the first and third interfaces F13, with no relation with the density correlation. They can give information on the lamellar thickness and long period but not on amorphous thickness since both the “self-correlation region” in the so-called “correlation function” and the first peak in IDF are dominated by F11, which does not include the parameter of amorphous thickness. With the revised procedure, the lamellar thickness and long period can be obtained readily from real scattering, whether for a lamellar two-phase system or a lamellar system with a broad thickness distribution. Based on the above-mentioned results, we suggest the removal of the concept of correlation function but the retention of IDF.
are similar to the correlation function and IDF in shape, respectively. Nevertheless, both of them are determined mainly by three items, i.e., the self-interference term of the first interface F11, the interference term between the first and second interfaces F12, and the interference term between the first and third interfaces F13, with no relation with the density correlation. They can give information on the lamellar thickness and long period but not on amorphous thickness since both the “self-correlation region” in the so-called “correlation function” and the first peak in IDF are dominated by F11, which does not include the parameter of amorphous thickness. With the revised procedure, the lamellar thickness and long period can be obtained readily from real scattering, whether for a lamellar two-phase system or a lamellar system with a broad thickness distribution. Based on the above-mentioned results, we suggest the removal of the concept of correlation function but the retention of IDF. 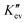 can be regarded as a new IDF, which represents the probability of finding an interface apart from the first interface of a lamellar stack at a distance of Z.
can be regarded as a new IDF, which represents the probability of finding an interface apart from the first interface of a lamellar stack at a distance of Z.
中文翻译:

聚合物层状晶体SAXS的傅立叶变换新方法
长期以来,半结晶聚合物的散射被认为是由于层状堆叠体中的电子密度相关。用于散射的傅立叶变换可以帮助获得相关函数和界面分布函数(IDF),从中可以获取结构信息。最近,我们发现,参与渐逝波(界面电子散射我我EV)是指实际原点(李等人,IUCrJ,2019,6,968-983)。有必要开发一种新的傅立叶变换方法以获得结构信息。在这项研究中,提出了一种与经典方法类似的方法。尽管如此,乘以q 2的目的或q 4是为了减少形状因数的影响,而傅立叶变换中的散射应为I i ev,大致等于结晶过程中增加的散射。通过傅立叶变换K ev和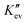 获得的函数在形状上分别类似于相关函数和IDF。然而,它们两者主要由三个项目决定,即第一接口F 11的自干扰项,第一接口F 12与第二接口F 12之间的干扰项以及第一接口F与第三接口F之间的干扰项。在图13中,与密度相关没有关系。他们可以给晶片厚度,周期长,但不是因为在所谓的“相关函数”无论是“自相关区域”,并在IDF第一峰非晶厚度由被主宰信息˚F 11,其中不包括非晶厚度的参数。通过修改后的程序,无论是层状两相系统还是厚度分布较宽的层状系统,都可以从真实散射中轻松获得层状厚度和较长的周期。基于上述结果,我们建议删除相关函数的概念,但保留IDF。
获得的函数在形状上分别类似于相关函数和IDF。然而,它们两者主要由三个项目决定,即第一接口F 11的自干扰项,第一接口F 12与第二接口F 12之间的干扰项以及第一接口F与第三接口F之间的干扰项。在图13中,与密度相关没有关系。他们可以给晶片厚度,周期长,但不是因为在所谓的“相关函数”无论是“自相关区域”,并在IDF第一峰非晶厚度由被主宰信息˚F 11,其中不包括非晶厚度的参数。通过修改后的程序,无论是层状两相系统还是厚度分布较宽的层状系统,都可以从真实散射中轻松获得层状厚度和较长的周期。基于上述结果,我们建议删除相关函数的概念,但保留IDF。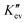 可以看作是一个新的IDF,它表示找到距离Z的层状堆栈的第一个界面以外的界面的概率。
可以看作是一个新的IDF,它表示找到距离Z的层状堆栈的第一个界面以外的界面的概率。
更新日期:2020-03-31
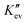 are similar to the correlation function and IDF in shape, respectively. Nevertheless, both of them are determined mainly by three items, i.e., the self-interference term of the first interface F11, the interference term between the first and second interfaces F12, and the interference term between the first and third interfaces F13, with no relation with the density correlation. They can give information on the lamellar thickness and long period but not on amorphous thickness since both the “self-correlation region” in the so-called “correlation function” and the first peak in IDF are dominated by F11, which does not include the parameter of amorphous thickness. With the revised procedure, the lamellar thickness and long period can be obtained readily from real scattering, whether for a lamellar two-phase system or a lamellar system with a broad thickness distribution. Based on the above-mentioned results, we suggest the removal of the concept of correlation function but the retention of IDF.
are similar to the correlation function and IDF in shape, respectively. Nevertheless, both of them are determined mainly by three items, i.e., the self-interference term of the first interface F11, the interference term between the first and second interfaces F12, and the interference term between the first and third interfaces F13, with no relation with the density correlation. They can give information on the lamellar thickness and long period but not on amorphous thickness since both the “self-correlation region” in the so-called “correlation function” and the first peak in IDF are dominated by F11, which does not include the parameter of amorphous thickness. With the revised procedure, the lamellar thickness and long period can be obtained readily from real scattering, whether for a lamellar two-phase system or a lamellar system with a broad thickness distribution. Based on the above-mentioned results, we suggest the removal of the concept of correlation function but the retention of IDF. 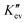 can be regarded as a new IDF, which represents the probability of finding an interface apart from the first interface of a lamellar stack at a distance of Z.
can be regarded as a new IDF, which represents the probability of finding an interface apart from the first interface of a lamellar stack at a distance of Z.
中文翻译:

聚合物层状晶体SAXS的傅立叶变换新方法
长期以来,半结晶聚合物的散射被认为是由于层状堆叠体中的电子密度相关。用于散射的傅立叶变换可以帮助获得相关函数和界面分布函数(IDF),从中可以获取结构信息。最近,我们发现,参与渐逝波(界面电子散射我我EV)是指实际原点(李等人,IUCrJ,2019,6,968-983)。有必要开发一种新的傅立叶变换方法以获得结构信息。在这项研究中,提出了一种与经典方法类似的方法。尽管如此,乘以q 2的目的或q 4是为了减少形状因数的影响,而傅立叶变换中的散射应为I i ev,大致等于结晶过程中增加的散射。通过傅立叶变换K ev和
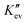 获得的函数在形状上分别类似于相关函数和IDF。然而,它们两者主要由三个项目决定,即第一接口F 11的自干扰项,第一接口F 12与第二接口F 12之间的干扰项以及第一接口F与第三接口F之间的干扰项。在图13中,与密度相关没有关系。他们可以给晶片厚度,周期长,但不是因为在所谓的“相关函数”无论是“自相关区域”,并在IDF第一峰非晶厚度由被主宰信息˚F 11,其中不包括非晶厚度的参数。通过修改后的程序,无论是层状两相系统还是厚度分布较宽的层状系统,都可以从真实散射中轻松获得层状厚度和较长的周期。基于上述结果,我们建议删除相关函数的概念,但保留IDF。
获得的函数在形状上分别类似于相关函数和IDF。然而,它们两者主要由三个项目决定,即第一接口F 11的自干扰项,第一接口F 12与第二接口F 12之间的干扰项以及第一接口F与第三接口F之间的干扰项。在图13中,与密度相关没有关系。他们可以给晶片厚度,周期长,但不是因为在所谓的“相关函数”无论是“自相关区域”,并在IDF第一峰非晶厚度由被主宰信息˚F 11,其中不包括非晶厚度的参数。通过修改后的程序,无论是层状两相系统还是厚度分布较宽的层状系统,都可以从真实散射中轻松获得层状厚度和较长的周期。基于上述结果,我们建议删除相关函数的概念,但保留IDF。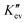 可以看作是一个新的IDF,它表示找到距离Z的层状堆栈的第一个界面以外的界面的概率。
可以看作是一个新的IDF,它表示找到距离Z的层状堆栈的第一个界面以外的界面的概率。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号