当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Monatsh. Chem.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Monitoring of n-butanol vapors biofiltration process using an electronic nose combined with calibration models.
Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly ( IF 1.7 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-10 , DOI: 10.1007/s00706-018-2243-6 Bartosz Szulczyński 1 , Piotr Rybarczyk 1 , Jacek Gębicki 1
中文翻译:

使用电子鼻结合校准模型监测正丁醇蒸汽生物过滤过程。

Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly ( IF 1.7 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-10 , DOI: 10.1007/s00706-018-2243-6 Bartosz Szulczyński 1 , Piotr Rybarczyk 1 , Jacek Gębicki 1
Affiliation
Abstract
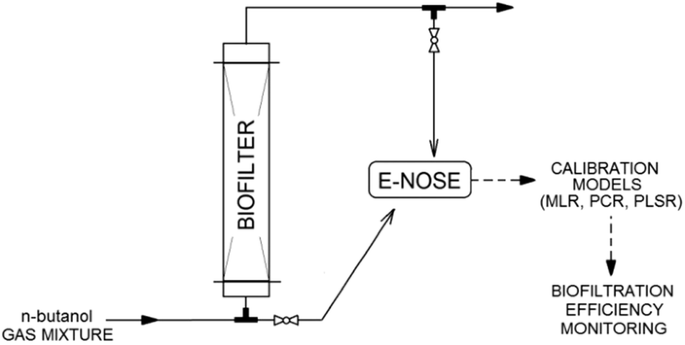
Malodorous odors, by definition, are unpleasant, irritating smells being a mixture of volatile chemical compounds that can be sensed at low concentrations. Due to the increasing problem of odor nuisance associated with odor sensations, and thus the need to remove them from the air, deodorization techniques are commonly used. Biofiltration is one of the methods of reducing odorants in the air stream. In the paper, the possibility of using an electronic nose as an alternative method to gas chromatography for the online monitoring and evaluation of efficiency of the n-butanol vapors biofiltration process in a transient state was investigated. Three calibration models were used in the research, i.e., multiple linear regression, principal component regression, and partial least-square regression. The obtained results were compared with the theoretical values.Graphical abstract

中文翻译:

使用电子鼻结合校准模型监测正丁醇蒸汽生物过滤过程。
摘要
恶臭气味,顾名思义,是一种令人不快、刺激性的气味,是一种挥发性化合物的混合物,可以在低浓度下被感知。由于与气味感觉相关的气味滋扰问题日益严重,因此需要将其从空气中去除,因此通常使用除臭技术。生物过滤是减少气流中气味的方法之一。在本文中,使用电子鼻作为气相色谱的替代方法进行在线监测和评估n效率的可能性研究了瞬态-丁醇蒸气生物过滤过程。研究中使用了三种校准模型,即多元线性回归、主成分回归和偏最小二乘回归。将所得结果与理论值进行比较。图形概要











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号