Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-11-16 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1434-7 Marko Mank , Philipp Welsch , Albert J. R. Heck , Bernd Stahl
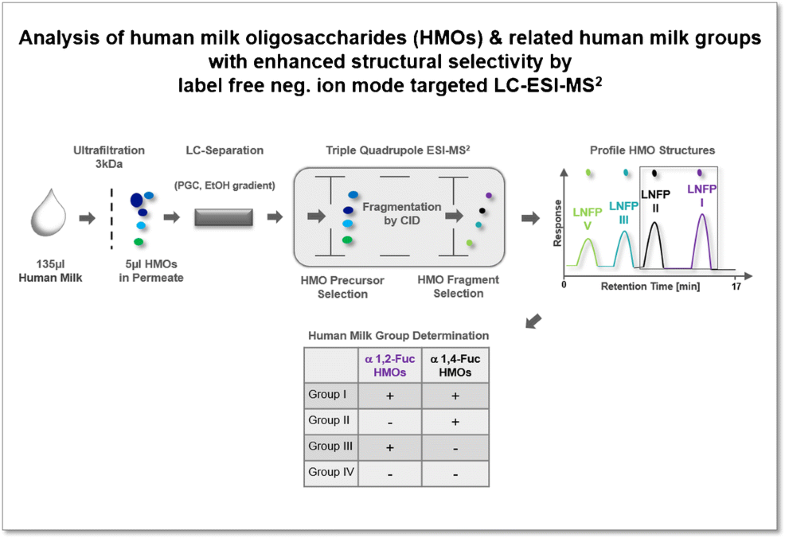
Human milk (HM) supports the healthy development of neonates and exerts many of its beneficial effects via contained free human milk oligosaccharides (HMOS). These HMOS exhibit a complexity and structural diversity that pose a significant analytical challenge. A detailed characterization of HMOS is essential as every individual structure may have a different function/activity. Certain HMOS isomers may even fundamentally differ in their biological function, and especially their characterization by LC or LC-MS is often impaired by co-elution phenomena. Thus, more efficient analytical methodologies with enhanced structural selectivity are required. Therefore, we developed a negative ion mode LC-ESI-MS2 approach featuring straightforward sample preparation, environmentally friendly EtOH gradient elution, and enhanced, semiquantitative characterization of distinct native HMOS by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). Our MRM-LC-MS setup takes advantage of highly selective, glycan configuration-dependent collision-induced dissociation (CID) fragments to identify individual neutral and acidic HMOS. Notably, many human milk oligosaccharide isomers could be distinguished in a retention time-independent manner. This contrasts with other contemporary MRM approaches relying on rather unspecific MRM transitions. Our method was used to determine the most abundant human milk tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexaoses semiquantitatively in a single LC-MS assay. Detected HMO structures included fucosyllactoses (e.g., 2′-FL), lacto-N-difucotetraose (LDFT), lacto-N-tetraoses (LNTs), lacto-N-fucopentaoses (e.g., LNFP I, LNFP II and III), lacto-N-difucohexaoses (LNDFHs) as well as sialyllactoses (SLs) and tentatively assigned blood group A and B tetrasaccharides from which correct human milk type assignment could be also demonstrated. Correctness of milk typing was validated for milk groups I–IV by high pressure anion exchange chromatography (HPAEC) coupled to pulsed amperometric detection (HPAEC-PAD).
ᅟ
中文翻译:

无标签靶向LC-ESI-MS
人乳(HM)支持新生儿的健康发育,并通过包含的游离人乳低聚糖(HMOS)发挥其许多有益作用。这些HMOS具有复杂性和结构多样性,这构成了重大的分析挑战。HMOS的详细表征至关重要,因为每个单独的结构都可能具有不同的功能/活动。某些HMOS异构体的生物学功能甚至可能根本上存在差异,尤其是通过LC或LC-MS表征通常会因共洗脱现象而受损。因此,需要具有增强的结构选择性的更有效的分析方法。因此,我们开发了一种负离子模式LC-ESI-MS 2该方法具有简单的样品制备,环保的EtOH梯度洗脱以及通过多反应监测(MRM)增强的独特天然HMOS的半定量表征。我们的MRM-LC-MS设置利用了高选择性,依赖于聚糖构型的碰撞诱导解离(CID)片段来识别单个中性和酸性HMOS。值得注意的是,许多人乳低聚糖异构体可以以不依赖保留时间的方式加以区分。这与依赖于非特定的MRM转换的其他当代MRM方法形成对比。我们的方法用于在单个LC-MS分析中半定量测定最丰富的人乳三,四,五和六糖。检测到的HMO结构包括岩藻糖基内酰胺酶(例如2'-FL),乳酸N-difucotetraose(LDFT),lacto- N -tetraoses(LNTs),lacto- N -fucopentaoses(例如LNFP I,LNFP II和III),lacto- N -difucohexaoses(LNDFHs)以及唾液乳糖(SLs)和暂定分配还可以证明A和B型血中的四糖具有正确的人乳类型分配。通过高压阴离子交换色谱法(HPAEC)和脉冲安培检测(HPAEC-PAD)验证了I–IV牛奶组牛奶分类的正确性。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号