Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-10-29 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1421-z Marco Beccaria , Flavio A. Franchina , Mavra Nasir , Theodore Mellors , Jane E. Hill , Giorgia Purcaro
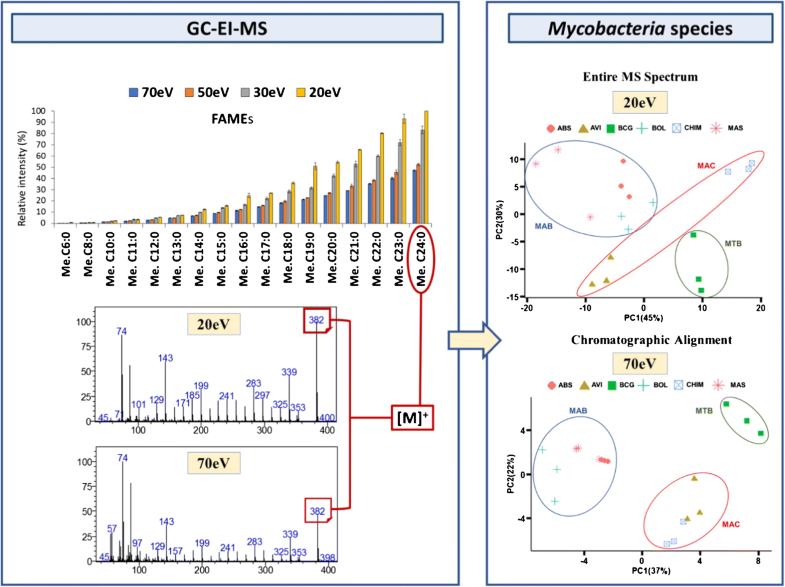
Gas chromatography (GC) coupled with electron ionization (EI) mass spectrometry (MS) is a well-established technique for the analysis of volatile and semi-volatile compounds. The main advantage is the highly repeatable fragmentation of the compounds into the ion source, generating intense and diagnostic fragmentation when the ionization is performed at 70 eV; this is considered the standard ionization condition and has been used for creating many established databases, which are of great support in the analyte identification process. However, such an intense fragmentation often causes the loss of the molecular ion or more diagnostic ions, which can be detrimental for the identification of homologous series or isomers, as for instance fatty acids. To obtain this information chemical or soft ionization can be used, but dedicated ion sources and conditions are required. In this work, we explored different ionization voltages in GC–EI–MS to preserve the intensity of the molecular ion using a conventional quadrupole MS. Twenty, 30, 50, and 70 eV were tested using a mixture of fatty acid methyl esters standards. Intensity and repeatability of the most informative ions were compared. Twenty and 70 eV were then used to analyze the fatty acid composition of six different strains of mycobacteria. Two approaches were used for elaborating the data: (1) a single average spectrum of the entire chromatogram was derived, which can be considered (in terms of concept) as a direct EI–MS analysis; (2) the actual chromatographic separation of the compounds was considered after automatic alignment. The results obtained are discussed herein.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用GC-MS中不同电离能的分枝杆菌脂肪酸谱研究
气相色谱(GC)与电子电离(EI)质谱(MS)结合使用是一种成熟的技术,用于分析挥发性和半挥发性化合物。主要优点是化合物在离子源中的重复性很高,可在70 eV进行电离时产生强烈的诊断性碎片。这被认为是标准电离条件,并已用于创建许多已建立的数据库,这些数据库在分析物识别过程中提供了大力支持。然而,这种强烈的断裂常常导致分子离子或更多诊断离子的损失,这对于鉴定同源系列或异构体(例如脂肪酸)可能是有害的。为了获得此信息,可以使用化学或软电离,但是需要专用的离子源和条件。在这项工作中,我们使用传统的四极杆质谱仪探索了GC-EI-MS中不同的电离电压,以保持分子离子的强度。使用脂肪酸甲酯标准混合物测试了20、30、50和70 eV。比较了最有用的离子的强度和可重复性。然后使用20和70 eV分析六种不同分枝杆菌菌株的脂肪酸组成。两种方法用于详细说明数据:(1)得出整个色谱图的单个平均光谱,可以将其视为直接的EI-MS分析(就概念而言);(2)自动比对后考虑了化合物的实际色谱分离。本文讨论了获得的结果。我们使用传统的四极杆质谱仪在GC–EI–MS中探索了不同的电离电压,以保持分子离子的强度。使用脂肪酸甲酯标准混合物测试了20、30、50和70 eV。比较了最有用的离子的强度和可重复性。然后使用20和70 eV分析六种不同分枝杆菌菌株的脂肪酸组成。两种方法用于详细说明数据:(1)得出整个色谱图的单个平均光谱,可以将其视为直接的EI-MS分析(就概念而言);(2)自动比对后考虑了化合物的实际色谱分离。本文讨论了获得的结果。我们使用传统的四极杆质谱仪在GC–EI–MS中探索了不同的电离电压,以保持分子离子的强度。使用脂肪酸甲酯标准混合物测试了20、30、50和70 eV。比较了最有用的离子的强度和可重复性。然后使用20和70 eV分析六种不同分枝杆菌菌株的脂肪酸组成。两种方法用于详细说明数据:(1)得出整个色谱图的单个平均光谱,可以将其视为直接的EI-MS分析(就概念而言);(2)自动比对后考虑了化合物的实际色谱分离。本文讨论了获得的结果。

ᅟ









































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号