Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-17 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1310-5 Shengnan Xu , Jie Ding , Ligang Chen
A new fluorescent probe based on graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) combined with molecularly imprinted silica was successfully fabricated and used to selectively recognize chlortetracycline (CTC). The g-C3N4 used in this study has the characteristics of low toxicity and high chemical stability. This synthetic composite was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, UV spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and fluorescence spectroscopy. The material was used to detect CTC by the fluorescence quenching technique. The fluorescence quenching was due to g-C3N4 and the benzene ring of CTC through π–π electron donor–acceptor interaction and electrostatic force. Hydrogen bonds formed between CTC and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane during the polymerization process. Eventually, a considerable amount of selective recognition holes were formed in the composite material and could specifically recognize the template molecule CTC. In addition, the probe strategy was successfully applied to milk analysis, and the recoveries ranged from 90.1% to 95.7%, with relative standard deviations of 1.8–2.8%; the detection limit for CTC was 8 ng mL-1. The results indicate that this method combined the sensitivity of fluorescence detection with the excellent selectivity of a molecularly imprinted polymer. The new material can be widely used in the detection of dairy products.
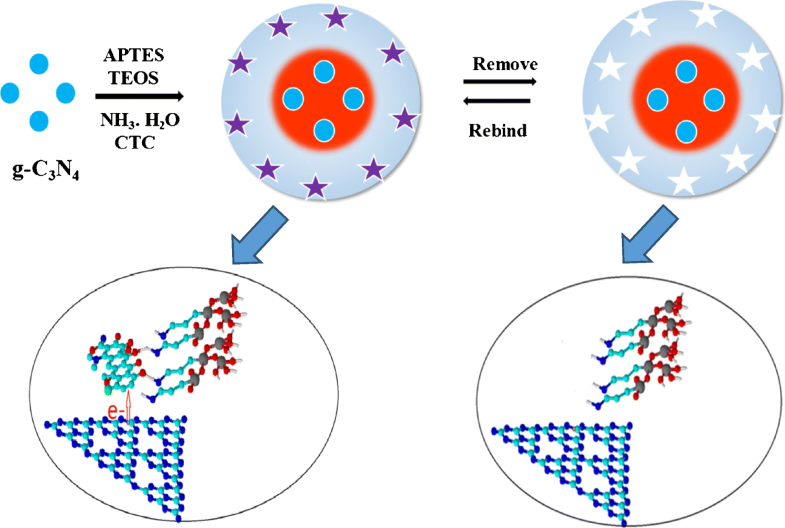
Schematic of synthesis of the MIP-capped g-C3N4 by sol-gel reaction
中文翻译:

一种基于分子印迹二氧化硅-石墨氮化碳复合物的用于检测金霉素的荧光材料
基于石墨化碳氮化物(gC 3 N 4)结合分子印迹二氧化硅的新型荧光探针已成功制备,并用于选择性识别金霉素。本研究中使用的gC 3 N 4具有低毒性和高化学稳定性的特点。通过透射电子显微镜,傅立叶变换红外光谱,UV光谱,X射线衍射和荧光光谱表征该合成复合材料。该材料用于通过荧光猝灭技术检测CTC。荧光猝灭是由于gC 3 N 4和四氯化碳的苯环通过π – π电子给体-受体相互作用和静电力。在聚合过程中,四氯化碳与3-氨基丙基三乙氧基硅烷之间形成了氢键。最终,在复合材料中形成了大量的选择性识别孔,它们可以特异性识别模板分子CTC。此外,该探针策略已成功应用于牛奶分析,其回收率从90.1%到95.7%,相对标准偏差为1.8-2.8%。CTC的检出限为8 ng mL -1。结果表明,该方法将荧光检测的灵敏度与分子印迹聚合物的出色选择性结合在一起。这种新材料可广泛用于乳制品的检测。

通过溶胶-凝胶反应合成MIP封端的gC 3 N 4的示意图











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号