Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-13 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1306-1 Paris Ning , Ronald Soong , Wolfgang Bermel , Daniel Lane , Myrna J. Simpson , André J. Simpson
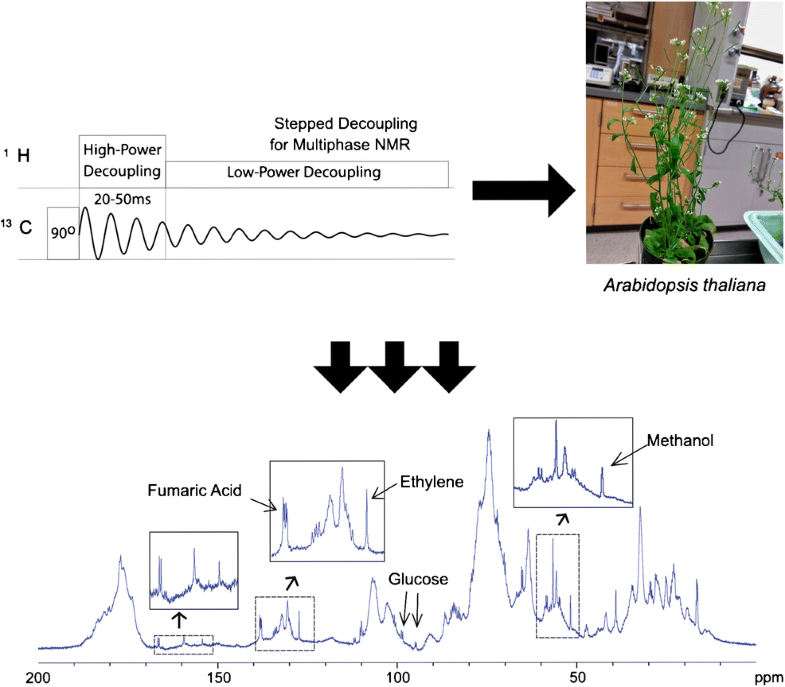
Many natural and environmental samples contain combinations of liquids, gels, and solids, yet quantification in the intact state and across multiple phases is highly challenging. Comprehensive multiphase nuclear magnetic resonance (CMP-NMR) combines all the capabilities of high-resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS), with the addition of full solids power handling, permitting all phases (i.e., mixtures of liquids, gels, and solids) to be studied and differentiated in intact samples without pre-treatment or extraction. Here, quantification in CMP-NMR is considered. As 1H NMR is considerably broadened in the solid-state, quantification is easier to achieve through 13C which can be observed easily in all the phases. Accurate 13C quantification requires effective 1H decoupling for all the phases, but each phase requires different decoupling conditions. To satisfy these conditions, a pulse sequence termed stepped decoupling is introduced. This sequence can be used to study all components under ideal decoupling conditions resulting in high-resolution spectra without truncation artifacts and provides accurate integrals of components in all phases. The approach is demonstrated on standards and then applied to natural samples including broccoli, soil, and Arabidopsis. The approach permits accurate quantification of chemical categories (for example total carbohydrates) as well as individual species (for example glucose). Further, as the samples are studied intact, volatile species such as methanol and ethylene which are normally hard to detect in plants can be easily quantified in Arabidopsis.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

许多天然和环境样品都包含液体,凝胶和固体的组合,但是完整状态和跨多个阶段的定量分析具有很高的挑战性。全面的多相核磁共振(CMP-NMR)结合了高分辨率魔角旋转(HR-MAS)的所有功能,并增加了全固体功率处理能力,允许所有相(即液体,凝胶和固体的混合物) ),无需进行预处理或提取即可在完整样品中进行研究和区分。在此,考虑了CMP-NMR中的定量。由于1 H NMR在固态时显着加宽,因此在13 C下更容易实现定量,这在所有相中都容易观察到。准确的13C量化要求所有相均进行有效的1 H解耦,但是每个相都需要不同的解耦条件。为了满足这些条件,引入了称为步进去耦的脉冲序列。该序列可用于研究理想去耦条件下的所有组分,从而得到无截断伪像的高分辨率光谱,并提供所有相中组分的准确积分。该方法已在标准中得到证明,然后应用于西兰花,土壤和拟南芥等天然样品。该方法允许对化学类别(例如总碳水化合物)以及单个物种(例如葡萄糖)进行准确定量。此外,由于对样品进行了完整的研究,通常可以在拟南芥中轻松量化通常难以在植物中检测到的挥发性物种,例如甲醇和乙烯。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号