Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.2 ) Pub Date : 2018-09-19 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-2058-z Elahe Honarvar 1 , Andre R. Venter 1
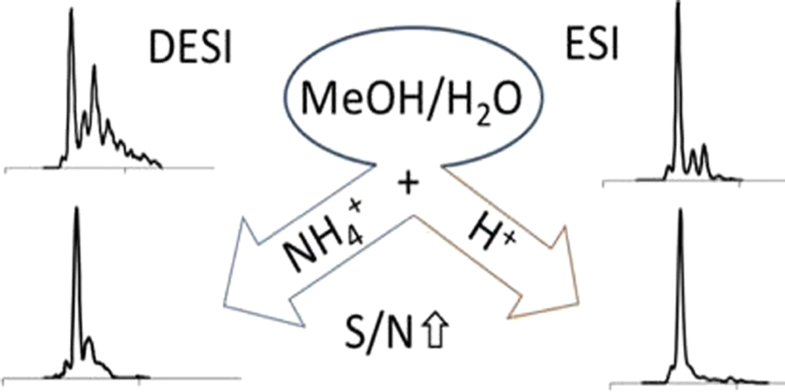
It is frequently said that DESI-MS follows a similar ionization mechanism as ESI because of similarities usually observed in their respective mass spectra. However, practical use of DESI-MS for protein analysis is limited to proteins with lower molecular weights (< 25 kDa) due to a mass-dependent loss in signal intensity. Here we investigated commonly used volatile acids and their ammonium salt buffers for DESI-MS analysis of protein. We noticed that, surprisingly, some additives influence the analysis differently in DESI compared to ESI. Improved signal intensities with both DESI and ESI were obtained when acetic and formic acid were added into aqueous methanol spray solvents with both DESI and ESI. On the other hand, while with ESI the addition of ammonium salts into spray solutions strongly reduced both signal and S/N, with DESI signal intensities and S/N were improved dramatically. Ammonium bicarbonate when used with DESI reduced the total amount of adduction and delivered excellent signal-to-noise ratios with high intensity; however, it also denatures protein. When native state protein mass spectra are preferred, ammonium acetate would also deliver reasonable adduct removal and improved S/N. The amount of total adduction of individual adducting species and of all species could not be correlated with differences in either solutions pH values or with proton affinities of the anions. An obvious difference between DESI and ESI mass spectrometry is the effects of protein solubility during droplet pickup (desorption), but differences in the sizes, velocities, and composition of ionizing droplets were also discussed as important factors.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

比较添加剂对解吸电喷雾(DESI)和电喷雾电离(ESI)之间蛋白质分析的影响
人们经常说,DESI-MS遵循与ESI类似的电离机理,因为通常在它们各自的质谱图中观察到相似性。但是,由于信号强度的质量依赖性损失,DESI-MS在蛋白质分析中的实际应用仅限于分子量较低(<25 kDa)的蛋白质。在这里,我们研究了常用的挥发性酸及其铵盐缓冲液,用于蛋白质的DESI-MS分析。我们注意到,令人惊讶的是,与ESI相比,某些添加剂在DESI中对分析的影响不同。当将乙酸和甲酸与DESI和ESI一起添加到含水甲醇喷雾溶剂中时,可以提高DESI和ESI的信号强度。另一方面,使用ESI时,在喷雾溶液中添加铵盐会大大降低信号和信噪比,DESI信号强度和信噪比得到了显着提高。与DESI一起使用的碳酸氢铵减少了加合的总量,并以高强度提供了出色的信噪比;但是,它也会使蛋白质变性。当天然状态的蛋白质的质谱是优选的,乙酸铵也将提供合理的加合物去除和改善的小号/ Ñ。单个加合物种和所有物种的总加合量均不能与溶液pH值的差异或阴离子的质子亲和力相关。DESI和ESI质谱法之间的一个明显区别是液滴吸收(解吸)过程中蛋白质溶解度的影响,但是电离液滴的大小,速度和组成方面的差异也被作为重要因素进行了讨论。

ᅟ



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号