Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-06-28 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-2006-y Christopher A. Zarzana 1 , Gary S. Groenewold 1 , Michael T. Benson 1 , James E. Delmore 1 , Tetsuya Tsuda 2 , Rika Hagiwara 3
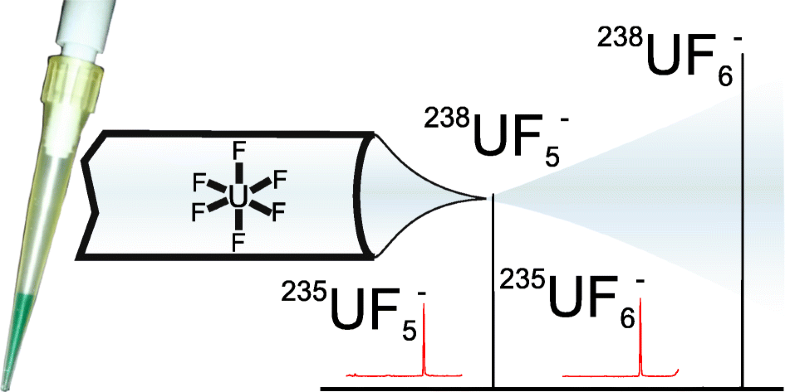
A new methodology for gas-phase uranium ion formation is described in which UO2 is dissolved in neat N-ethyl,N′-methylimidazolium fluorohydrogenate ionic liquid [EMIm+][F(HF)2.3−], yielding a blue-green solution. The solution was diluted with acetonitrile and then analyzed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. UF6− (a U(V) species) was observed at m/z = 352, and other than cluster ions derived from the ionic liquid, nothing else was observed. When the sample was analyzed using infusion desorption chemical ionization, UF6− was the base peak, and it was accompanied by a less intense UF5− that most likely was formed by elimination of a fluorine radical from UF6−. Formation of UF6− required dissolution of UO2 followed by or concurrent with oxidation of uranium from the + 4 to the + 5 state and finally formation of the fluorouranate. Dissolution of UO3 produced a bright yellow solution indicative of a U(VI) species; however, electrospray ionization did not produce abundant U-containing ions. The abundant UF6− provides a vehicle for accurate measurement of uranium isotopic abundances free from interference from minor isotopes of other elements and a convenient ion synthesis route that is needed gas-phase structure and reactivity studies like infrared multiphoton dissociation and ion-molecule dissociation and condensation reactions. The reactive fluorohydrogenate ionic liquid may also enable conversion of uranium in oxidic matrices into uranium fluorides that slowly oxidize to uranyl fluoride under ambient conditions, liberating the metal for facile measurement of isotope ratios without extensive chemical separations.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

通过在[1-乙基-3-甲基咪唑鎓]中氧化铀的溶解生产气相铀氟阴离子
描述了一种用于气相铀离子形成的新方法,其中UO 2溶解在纯净Ñ -乙基,Ñ '甲基咪唑fluorohydrogenate离子液体[EMIM + ] [F(HF)2.3 - ],得到蓝绿色溶液。将该溶液用乙腈稀释,然后通过电喷雾电离质谱分析。UF 6 - (一U(V)物种)在观察米/ ž = 352,并且比从所述离子液体导出簇离子以外,观察到没有别的。使用输液解吸化学电离当对样品进行分析,UF 6 -是基峰,并且它是伴随着较不强烈的UF 5 - ,最有可能是通过消除从UF自由基氟形成6 - 。UF的形成6 - UO的所需溶解2,随后或同时从+ 4铀氧化成+5状态并最终形成fluorouranate的。UO 3的溶解产生了明亮的黄色溶液,表明存在U(VI)物种。但是,电喷雾电离不能产生大量的含U离子。丰富的UF 6 -提供了一种精确测量铀同位素丰度的工具,不受其他元素的微量同位素干扰,并且提供了便捷的离子合成路线,这是气相结构和反应性研究(如红外多光子离解和离子分子离解和缩合反应)所必需的。反应性氢氟酸离子液体还可以使氧化基质中的铀转化为氟化铀,然后在环境条件下将其缓慢氧化为氟化铀酰,从而释放出金属以方便地进行同位素比测量,而无需进行广泛的化学分离。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号