Nano Research ( IF 9.5 ) Pub Date : 2018-09-03 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-018-2170-1 Sarah R. McKibbin , Sofie Yngman , Olivier Balmes , Bengt O. Meuller , Simon Tågerud , Maria E. Messing , Giuseppe Portale , Michael Sztucki , Knut Deppert , Lars Samuelson , Martin H. Magnusson , Edvin Lundgren , Anders Mikkelsen
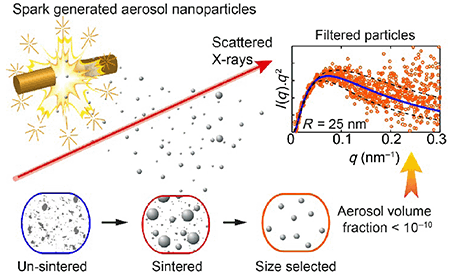
In-air epitaxy of nanostructures (Aerotaxy) has recently emerged as a viable route for fast, large-scale production. In this study, we use small-angle X-ray scattering to perform direct in-flight characterizations of the first step of this process, i.e., the engineered formation of Au and Pt aerosol nanoparticles by spark generation in a flow of N2 gas. This represents a particular challenge for characterization because the particle density can be extremely low in controlled production. The particles produced are examined during production at operational pressures close to atmospheric conditions and exhibit a lognormal size distribution ranging from 5–100 nm. The Au and Pt particle production and detection are compared. We observe and characterize the nanoparticles at different stages of synthesis and extract the corresponding dominant physical properties, including the average particle diameter and sphericity, as influenced by particle sintering and the presence of aggregates. We observe highly sorted and sintered spherical Au nanoparticles at ultra-dilute concentrations (< 5 × 105 particles/cm3) corresponding to a volume fraction below 3 × 10–10, which is orders of magnitude below that of previously measured aerosols. We independently confirm an average particle radius of 25 nm via Guinier and Kratky plot analysis. Our study indicates that with high-intensity synchrotron beams and careful consideration of background removal, size and shape information can be obtained for extremely low particle concentrations with industrially relevant narrow size distributions.
中文翻译:

空气中的纳米结构外延(Aerotaxy)最近成为快速,大规模生产的可行途径。在这项研究中,我们使用小角度X射线散射对该过程的第一步进行飞行中的直接表征,即,通过在N 2流中产生火花而设计形成Au和Pt气溶胶纳米颗粒。气体。对于表征而言,这代表了特别的挑战,因为在受控生产中颗粒密度可能极低。在生产过程中,在接近大气条件的工作压力下检查产生的颗粒,并显示出对数正态尺寸分布,范围为5–100 nm。比较了金和铂粒子的产生和检测。我们观察和表征了纳米颗粒在合成的不同阶段,并提取了相应的主要物理性能,包括平均粒径和球形度,这受颗粒烧结和聚集体的影响。我们观察到超稀疏浓度(<5×10 5粒子/ cm 3的高度分选和烧结的球形Au纳米粒子)对应的体积分数低于3×10 –10,这比先前测量的气溶胶的体积分数低几个数量级。我们通过Guinier和Kratky图分析独立地确认了25 nm的平均粒子半径。我们的研究表明,使用高强度同步加速器光束并仔细考虑背景去除的情况,可以获得具有工业相关的窄尺寸分布的极低颗粒浓度的尺寸和形状信息。












































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号