Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-04 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1255-8 Rime Michael-Jubeli , Ali Tfayli , Caroline Baudouin , Jean Bleton , Dominique Bertrand , Arlette Baillet-Guffroy
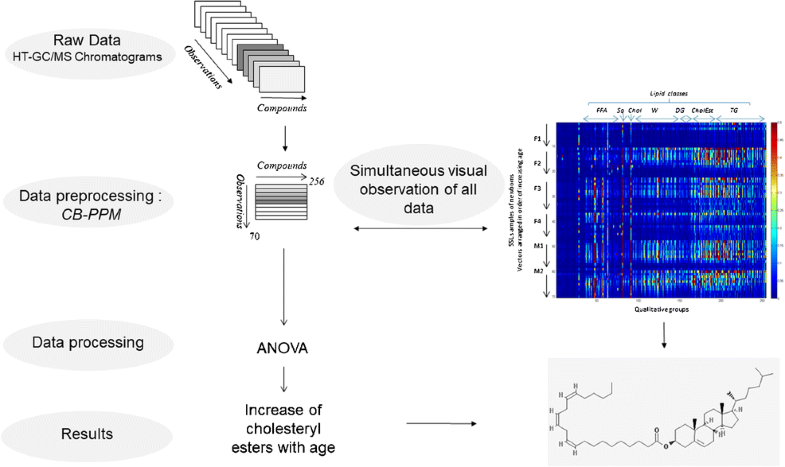
After life in utero and birth, the skin is submitted to an important process of adaptation to a relatively dry gaseous environment. Skin surface lipids (SSLs) contribute actively to the protection of the skin barrier. Within this context, our objective was to study the evolution of each lipid compound during the postnatal period. SSLs were collected from six newborns a few days after birth until the age of 6 months. Seventy samples were analyzed using high-temperature gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (HT-GC/MS). The use of separative techniques coupled to mass spectrometry for the analysis of samples containing complex mixtures of lipids generates a large volume of data which renders the results interpretation very difficult. In this study, we propose a new approach to handle the raw data, a clustering-based preprocessing method (CB-PPM), in order to achieve (1) volume reduction of data provided by each chromatogram without loss of information, (2) alignment of time retention shift between different runs, (3) clustering of mass spectra of the same molecule in one qualitative group, (4) and integration of all data into a single matrix to be explored by chemometric tools. This approach allowed us to gather data variations in 256 qualitative groups and therefore enabled us to highlight the variation of compounds including those of low intensity. Moreover, the representation of all data gathered in one matrix rendered reading of the results rapid and efficient. Thus, using this approach, we have demonstrated an increase of cholesterol esterification with epidermal fatty acids (C20 to C25) with age. This epidermis participation in SSL production at a molecular level in the first period of life has not been previously shown. These data can be very interesting for the development and improvement of products destined for the protection of infant skin.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

基于聚类的脂质组学数据预处理方法:从出生到六个月的新生儿皮肤表面脂质演变的应用
在子宫内出生并出生后,皮肤经历了适应相对干燥的气体环境的重要过程。皮肤表面脂质(SSL)对保护皮肤屏障有积极作用。在此背景下,我们的目标是研究每种脂类化合物在产后的演变过程。从出生后几天直到六个月大的六个新生儿中收集SSL。使用高温气相色谱-质谱联用技术(HT-GC / MS)分析了70个样品。使用分离技术与质谱联用来分析包含复杂脂质混合物的样品会产生大量数据,这使得结果解释非常困难。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种处理原始数据的新方法,一种基于聚类的预处理方法(CB-PPM),以实现(1)在不损失信息的情况下减少每个色谱图提供的数据的体积,(2)不同运行之间的保留时间偏移的对齐方式,(3)质量聚类同一分子在一个定性组中的质谱图(4),并将所有数据整合到一个矩阵中,以使用化学计量学工具进行探索。这种方法使我们能够收集256个定性组中的数据变化,因此使我们能够突出显示包括低强度化合物在内的化合物的变化。而且,在一个矩阵中收集的所有数据的表示使结果的读取快速而有效。因此,使用这种方法,我们证明了随着年龄的增长,表皮脂肪酸(C20至C25)的胆固醇酯化作用会增加。在生命的最初阶段,这种表皮在分子水平上参与SSL产生的过程尚未得到证实。这些数据对于开发和改进旨在保护婴儿皮肤的产品可能非常有趣。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号