Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-07-06 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1235-z George C. Rhoderick , Michael E. Kelley , Lyn Gameson , Kimberly J. Harris , Joseph T. Hodges
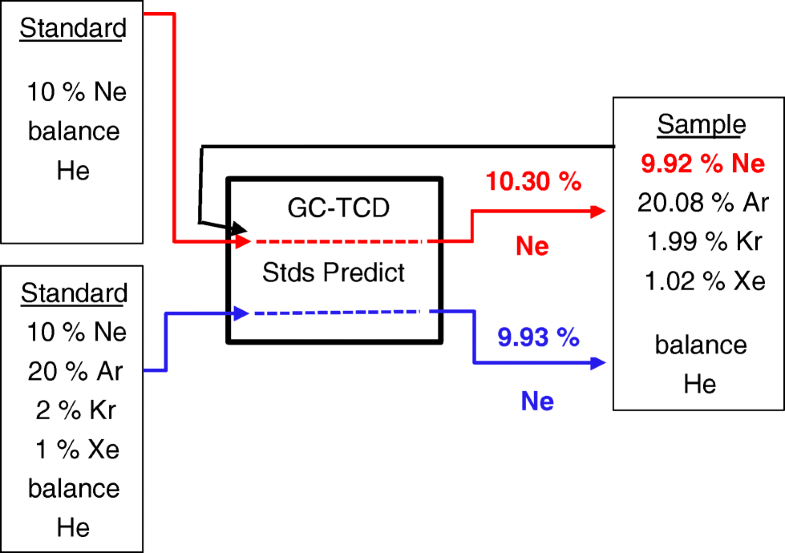
The noble gases, namely neon, argon, krypton and xenon, have many uses including in incandescent and gas discharge lighting, in plasma televisions, shielding gas in welding, in lasers for surgery and semiconductors, and in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lungs. When incorporating these noble gases in industries, especially the medical field, it is important to know accurately the composition of the noble gas mixture. Therefore, there is a need for accurate gas standards that can be used to determine the noble gas amount-of-substance fraction in the appropriate mixture application. A recent comparison of mixtures containing four noble gases in a helium balance showed mixed results among National Metrology Institutes. Significant differences, 0.7 to 3.8% relative, were seen in the analytical amount-of-substance assignments versus the gravimetric value of the noble gases in the comparison mixture when using “binary standards”, i.e. neon in helium, argon in helium and krypton in helium, as applied by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Post-comparison studies showed that when all four noble gases were included in the standards, the agreement between analytical and gravimetric values was within 0.05% relative. Further research revealed that different carrier gases (hydrogen, helium and nitrogen) resulted in varying differences between the analytical and gravimetric values assignments. This paper will discuss the findings of these analytical comparisons.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用具有热导检测功能的气相色谱仪分析稀有气体的问题
稀有气体,即氖气,氩气,k气和氙气,具有许多用途,包括白炽灯和气体放电灯,等离子电视,焊接中的保护气体,外科手术和半导体激光器以及磁共振成像(MRI)肺。在工业,特别是医疗领域中掺入这些稀有气体时,准确了解稀有气体混合物的组成非常重要。因此,需要可用于确定适当的混合物应用中的稀有气体物质分数的准确的气体标准。最近对氦平衡中包含四种稀有气体的混合物进行的比较显示,国家计量研究所的结果不一。显着差异,相对值为0.7至3.8%,在使用“二元标准”时,在分析混合物中稀有气体的分析物相对于稀有气体的重量值中可以看到,这是由美国国立科学研究院(National Institute of Institute)应用的氦中的氖,氦中的氩和氦中的k标准和技术。对比后研究表明,当所有四种稀有气体都包括在标准液中时,分析值与重量值之间的一致性在0.05%的相对范围内。进一步的研究表明,不同的载气(氢气,氦气和氮气)导致分析值和重量值分配之间的差异有所不同。本文将讨论这些分析比较的结果。美国国家标准技术研究院(National Institute of Standards and Technology)应用的氦气中的氩气和氦气中的k气。对比后研究表明,当所有四种稀有气体都包括在标准液中时,分析值与重量值之间的一致性在0.05%的相对范围内。进一步的研究表明,不同的载气(氢气,氦气和氮气)导致分析值和重量值分配之间的差异有所不同。本文将讨论这些分析比较的结果。美国国家标准技术研究院(National Institute of Standards and Technology)应用的氦气中的氩气和氦气中的k气。对比后研究表明,当所有四种稀有气体都包括在标准液中时,分析值与重量值之间的一致性在0.05%的相对范围内。进一步的研究表明,不同的载气(氢气,氦气和氮气)导致分析值和重量值分配之间的差异有所不同。本文将讨论这些分析比较的结果。氦和氮)导致分析值和重量值分配之间的差异。本文将讨论这些分析比较的结果。氦和氮)导致分析值和重量值分配之间的差异。本文将讨论这些分析比较的结果。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号