Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-06-07 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1997-8 Hanxue Xia 1 , Yong Zhang 1 , Athula B. Attygalle 1
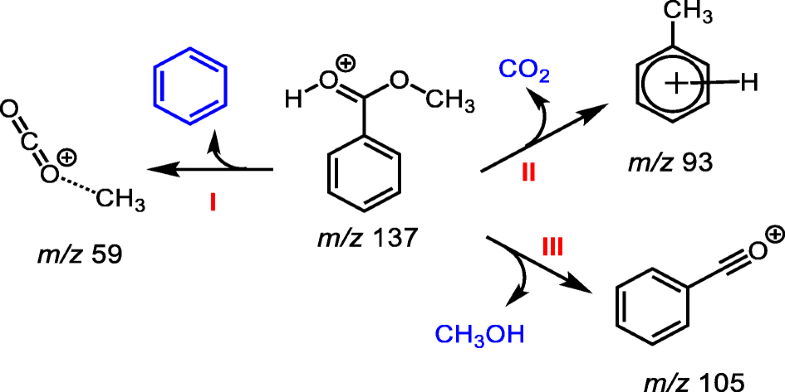
Protonated methyl benzoate, upon activation, fragments by three distinct pathways. The m/z 137 ion for the protonated species generated by helium-plasma ionization (HePI) was mass-selected and subjected to collisional activation. In one fragmentation pathway, the protonated molecule generated a product ion of m/z 59 by eliminating a molecule of benzene (Pathway I). The m/z 59 ion (generally recognized as the methoxycarbonyl cation) produced in this way, then formed a methyl carbenium ion in situ by decarboxylation, which in turn evoked an electrophilic aromatic addition reaction on the benzene ring by a termolecular process to generate the toluenium cation (Pathway II). Moreover, protonated methyl benzoate undergoes also a methanol loss (Pathway III). However, it is not a simple removal of a methanol molecule after a protonation on the methoxy group. The incipient proton migrates to the ring and randomizes to a certain degree before a subsequent transfer of one of the ring protons to the alkoxy group for the concomitant methanol elimination. The spectrum recorded from deuteronated methyl benzoate showed two peaks at m/z 105 and 106 for the benzoyl cation at a ratio of 2:1, confirming the charge-imparting proton is mobile. However, the proton transfer from the benzenium intermediate to the methoxy group for the methanol loss occurs before achieving a complete state of scrambling.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

苯甲酸质子化的气相裂解反应的实验和理论研究:苯,二氧化碳和甲醇的中性消除
活化后,质子化的苯甲酸甲酯通过三个不同的途径断裂。对通过氦等离子体电离(HePI)生成的质子化物质的m / z 137离子进行了质量选择,并进行了碰撞活化。在一个断裂途径中,质子化的分子通过消除苯分子产生了m / z 59的产物离子(途径I)。该M / Z以这种方式产生的59离子(通常被认为是甲氧羰基阳离子),然后通过脱羧原位形成甲基碳正离子,然后通过分子过程在苯环上引发亲电芳族加成反应,生成甲苯阳离子(途径II)。此外,质子化的苯甲酸甲酯也经历甲醇损失(途径III)。然而,在甲氧基上质子化之后,不是简单地除去甲醇分子。初始质子迁移至环并随机化至一定程度,然后环质子之一随后转移至烷氧基以伴随甲醇消除。氘化苯甲酸甲酯记录的光谱在m / z处显示两个峰苯甲酰基阳离子的比率为105和106,比率为2:1,这证明赋予电荷的质子是可移动的。然而,在达到完全加扰状态之前,发生了从苯中间体中间质子转移至甲氧基的甲醇损失。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号