Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-29 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1981-3 Troy J. Attard 1, 2 , Melissa D. Carter 3 , Mengxuan Fang 1 , Rudolph C. Johnson 3 , Gavin E. Reid 1, 2, 4
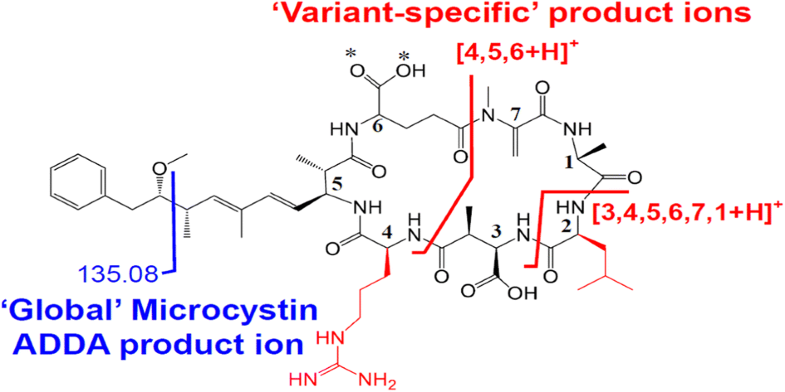
Microcystin (MC) peptides produced by cyanobacteria pose a hepatotoxic threat to human health upon ingestion from contaminated drinking water. While rapid MC identification and quantification in contaminated body fluids or tissue samples is important for patient treatment and outcomes, conventional immunoassay-based measurement strategies typically lack the specificity required for unambiguous determination of specific MC variants, whose toxicity can significantly vary depending on their structures. Furthermore, the unambiguous identification and accurate quantitation of MC variants using tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS)-based methods can be limited due to a current lack of appropriate stable isotope-labeled internal standards. To address these limitations, we have systematically examined here the sequence and charge state dependence to the formation and absolute abundance of both “global” and “variant-specific” product ions from representative MC-LR, MC-YR, MC-RR, and MC-LA peptides, using higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD)-MS/MS, ion-trap collision-induced dissociation (CID)-MS/MS and CID-MS3, and 193 nm ultraviolet photodissociation (UPVD)-MS/MS. HCD-MS/MS was found to provide the greatest detection sensitivity for both global and variant-specific product ions in each of the MC variants, except for MC-YR where a variant-specific product uniquely formed via UPVD-MS/MS was observed with the greatest absolute abundance. A simple methodology for the preparation and characterization of 18O-stable isotope-labeled MC reference materials for use as internal standards was also developed. Finally, we have demonstrated the applicability of the methods developed herein for absolute quantification of MC-LR present in human urine samples, using capillary scale liquid chromatography coupled with ultra-high resolution / accurate mass spectrometry and HCD-MS/MS.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

碰撞诱导和紫外光解离串联质谱分析微囊藻毒素肽的结构表征和绝对定量
蓝细菌产生的微囊藻毒素(MC)肽摄入被污染的饮用水后,会对人类健康构成肝毒性威胁。尽管对受污染的体液或组织样本中的MC进行快速识别和定量对于患者治疗和治疗结果很重要,但传统的基于免疫测定的测量策略通常缺乏明确确定特定MC变体所需的特异性,而这些MC变体的毒性可能会因其结构而异。此外,由于目前缺乏合适的稳定同位素标记的内标,使用串联质谱(MS / MS)的方法对MC变体的明确鉴定和准确定量可能会受到限制。为了解决这些限制,3和193 nm紫外光解离(UPVD)-MS / MS。发现HCD-MS / MS对每个MC变体中的整体离子和变体特异性产物离子均提供最大的检测灵敏度,但MC-YR除外,在MC-YR中观察到通过UPVD-MS / MS唯一形成的变体特异性产物具有最大的绝对丰度。还开发了一种简单的方法来制备和表征18种O稳定同位素标记的MC参考材料,以用作内标。最后,我们已经证明,本文开发的方法可用于毛细管定量液相色谱结合超高分辨率/精确质谱和HCD-MS / MS对人尿液样品中存在的MC-LR进行绝对定量。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号