Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-25 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1982-2 Kelsey A. Morrison 1 , Brad K. Bendiak 2 , Brian H. Clowers 1
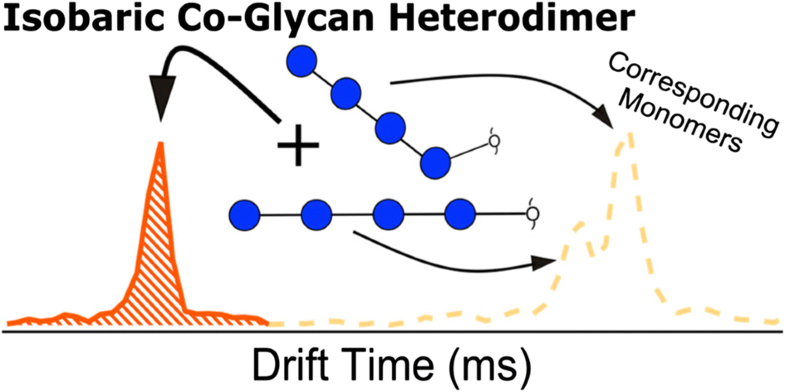
Adduction of multivalent metal ions to glycans has been shown in recent years to produce altered tandem mass spectra with collision-induced dissociation, electron transfer techniques, and photon-based fragmentation approaches. However, these approaches assume the presence of a well-characterized precursor ion population and do not fully account for the possibility of multimeric species for select glycan-metal complexes. With the use of ion mobility separations prior to mass analysis, doubly charged dimers are not necessarily problematic for tandem MS experiments given that monomer and dimer drift times are sufficiently different. However, multistage mass spectrometric experiments performed on glycans adducted to multivalent metals without mobility separation can yield chimeric fragmentation spectra that are essentially a superposition of the fragments from both the monomeric and dimeric adducts. For homodimeric adducts, where the dimer contains two of the same glycan species, this is less of a concern but if heterodimers can form, there exists the potential for erroneous and misleading fragment ions to appear if a heterodimer containing two different isomers is fragmented along with a targeted monomer. We present an assessment of heterodimer formation between a series of six tetrasaccharides, of which three are isomers, adducted with cobalt(II) and a monodeuterated tetrasaccharide. Using ion mobility separations prior to single-stage and tandem mass analysis, the data shown demonstrate that heterodimeric species can indeed form, and that ion mobility separations are highly necessary prior to using tandem techniques on metal-glycan adducts.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

通过同位素标记和离子迁移质谱法评估二聚金属糖加合物
近年来,已显示出多价金属离子与聚糖的加成可通过碰撞诱导的解离,电子转移技术和基于光子的碎裂方法产生改变的串联质谱。但是,这些方法假定存在特征明确的前体离子,并且不能完全考虑选择聚糖-金属配合物的多聚体物种的可能性。在质量分析之前使用离子淌度分离,假设单体和二聚体的漂移时间足够不同,双电荷二聚体对于串联MS实验并不一定是有问题的。然而,在不迁移率分离的情况下,对加成于多价金属上的聚糖进行的多级质谱实验可以产生嵌合片段化光谱,该片段基本上是单体加合物和二聚体加合物的片段的叠加。对于同二聚体加合物,其中二聚体包含两个相同的聚糖种类,则不必担心,但是如果可以形成异二聚体,则如果包含两个不同异构体的异二聚体随同被片段化,则存在出现错误和误导性碎片离子的可能性。目标单体。我们提出了一系列的六个四糖之间的异二聚体形成的评估,其中三个异构体与钴(II)加成单氘代四糖加成。在单级和串联质量分析之前使用离子迁移率分离,

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号