Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-23 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1900-7 Rini Roy 1 , Evelyn Ang 1, 2 , Emy Komatsu 1 , Ronald Domalaon 1 , Adrien Bosseboeuf 3 , Jean Harb 4 , Sylvie Hermouet 3 , Oleg Krokhin 1, 2 , Frank Schweizer 1 , Hélène Perreault 1
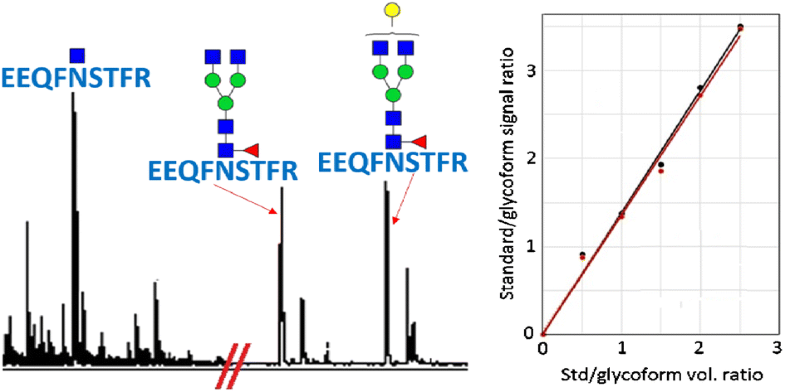
Immunoglobulins, such as immunoglobulin G (IgG), are of prime importance in the immune system. Polyclonal human IgG comprises four subclasses, of which IgG1 and IgG2 are the most abundant in healthy individuals. In an effort to develop an absolute MALDI-ToF-MS quantitative method for these subclasses and their Fc N-glycoforms, (glyco)peptides were synthesized using a solid-phase approach and used as internal standards. Tryptic digest glycopeptides from monoclonal IgG1 and IgG2 samples were first quantified using EEQYN(GlcNAc)STYR and EEQFN(GlcNAc)STFR standards, respectively. For IgG1, a similar glycopeptide where tyrosine (Y) was isotopically labelled was used to quantify monoclonal IgG1 that had been treated with the enzyme Endo-F2, i.e., yielding tryptic glycopeptide EEQYN(GlcNAc)STYR. The next step was to quantify single subclasses within polyclonal human IgG samples. Although ion abundances in the MALDI spectra often showed higher signals for IgG2 than IgG1, depending on the spotting solvent used, determination of amounts using the newly developed quantitative method allowed to obtain accurate concentrations where IgG1 species were predominant. It was observed that simultaneous analysis of IgG1 and IgG2 yielded non-quantitative results and that more success was obtained when subclasses were quantified one by one. More experiments served to assess the respective extraction and ionization efficiencies of EEQYNSTYR/EEQFNSTFR and EEQYN(GlcNAc)STYR/EEQFN(GlcNAc)STFR mixtures under different solvent and concentration conditions.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用合成Fc肽和糖肽对两种人IgG亚类糖型的绝对定量
免疫球蛋白,例如免疫球蛋白G(IgG),在免疫系统中至关重要。多克隆人IgG包含四个亚类,其中IgG1和IgG2在健康个体中含量最高。为了开发针对这些亚类及其Fc N的绝对MALDI-ToF-MS定量方法-糖形式,(糖)肽是使用固相方法合成的,并用作内标。首先分别使用EEQYN(GlcNAc)STYR和EEQFN(GlcNAc)STFR标准品定量来自单克隆IgG1和IgG2样品的胰蛋白酶消化糖肽。对于IgG1,使用类似的糖肽(其中酪氨酸(Y)被同位素标记)用于定量已用酶Endo-F2处理的单克隆IgG1,即产生胰蛋白酶糖肽EEQYN(GlcNAc)STYR。下一步是定量多克隆人IgG样品中的单个亚类。尽管MALDI谱中的离子丰度通常显示比IgG1高的IgG2信号,但取决于所用的点样溶剂,使用新开发的定量方法对量进行测定可以得到以IgG1为主要成分的准确浓度。可以观察到,同时分析IgG1和IgG2产生了非定量结果,并且当亚类一一定量时获得了更大的成功。更多实验用于评估在不同溶剂和浓度条件下EEQYNSTYR / EEQFNSTFR和EEQYN(GlcNAc)STYR / EEQFN(GlcNAc)STFR混合物各自的萃取和电离效率。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号