Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-17 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1063-1 Ziping Liu , Shasha Liu
In this work, a novel simple fluorescent biosensor for the highly sensitive and selective detection of adrenaline was established. Firstly, water-soluble CuInS2 quantum dots (QDs) capped by L-Cys were synthesized via a hydrothermal synthesis method. Then, the positively charged adrenaline was assembled on the surface of CuInS2 QDs due to the electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding, which led to the formation of adrenaline-CuInS2 QD (Adr-CuInS2 QD) electrostatic complexes. Tyrosinase (TYR) can catalyze adrenaline to generate H2O2, and additionally oxidize the adrenaline to adrenaline quinone. Both the H2O2 and the adrenaline quinone can quench the fluorescence of the CuInS2 QDs through the electron transfer (ET) process. Thus, the determination of adrenaline could be facilely achieved by taking advantage of the fluorescence “turn off” feature of CuInS2 QDs. Under the optimum conditions, the fluorescence quenching ratio If/If0 (If and If0 were the fluorescence intensity of Adr-CuInS2 QDs in the presence and absence of TYR, respectively) was proportional to the logarithm of adrenaline concentration in the range of 1 × 10−8–1 × 10−4 mol L−1 with the detection limit of 3.6 nmol L−1. The feasibility of the proposed biosensor in real sample assay was also studied and satisfactory results were obtained. Significantly, the proposed fluorescent biosensor can also be utilized to screen TYR inhibitors.
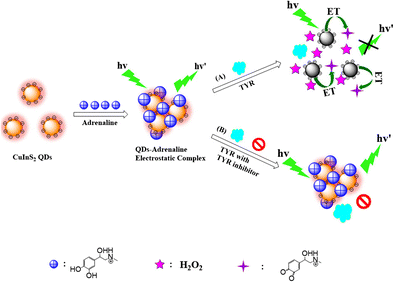
Schematic illustration of the fluorescent biosensor for adrenaline detection (A) and tyrosinase inhibitor screening (B).
中文翻译:

用于肾上腺素检测和酪氨酸酶抑制剂筛选的新型荧光生物传感器
在这项工作中,建立了用于肾上腺素的高灵敏度和选择性检测的新型简单荧光生物传感器。首先,通过水热合成法合成了由L-Cys覆盖的水溶性CuInS 2量子点(QDs)。然后,由于静电相互作用和氢键作用,将带正电的肾上腺素组装在CuInS 2 QD的表面上,这导致形成肾上腺素-CuInS 2 QD(Adr-CuInS 2 QD)静电配合物。酪氨酸酶(TYR)可以催化肾上腺素生成H 2 O 2,并将肾上腺素氧化为肾上腺素醌。既是H 2 O 2肾上腺素醌可通过电子转移(ET)过程猝灭CuInS 2 QDs的荧光。因此,可以通过利用CuInS 2 QD的荧光“关闭”功能轻松地实现肾上腺素的测定。在最佳条件下,荧光猝灭比I f / I f0(I f和I f0分别是存在和不存在TYR时Adr-CuInS 2 QD的荧光强度)与肾上腺素浓度的对数成正比。范围1×10 -8 –1×10 -4 mol L -1检测限为3.6 nmol L -1。还研究了所提出的生物传感器在实际样品分析中的可行性,并获得了满意的结果。重要的是,提出的荧光生物传感器也可以用于筛选TYR抑制剂。

用于肾上腺素检测的荧光生物传感器(A)和酪氨酸酶抑制剂筛选(B)的示意图。









































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号