Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-17 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1007-9 Agnieszka Martyna , Hans-Eike Gäbler , Andreas Bahr , Grzegorz Zadora
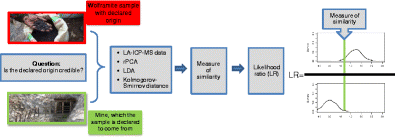
Wolframite has been specified as a ‘conflict mineral’ by a U.S. Government Act, which obliges companies that use these minerals to report their origin. Minerals originating from conflict regions in the Democratic Republic of the Congo shall be excluded from the market as their illegal mining, trading, and taxation are supposed to fuel ongoing violent conflicts. The German Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR) developed a geochemical fingerprinting method for wolframite based on laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Concentrations of 46 elements in about 5300 wolframite grains from 64 mines were determined. The issue of verifying the declared origins of the wolframite samples may be framed as a forensic problem by considering two contrasting hypotheses: the examined sample and a sample collected from the declared mine originate from the same mine (H1), and the two samples come from different mines (H2). The solution is found using the likelihood ratio (LR) theory. On account of the multidimensionality, the lack of normal distribution of data within each sample, and the huge within-sample dispersion in relation to the dispersion between samples, the classic LR models had to be modified. Robust principal component analysis and linear discriminant analysis were used to characterize samples. The similarity of two samples was expressed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov distances, which were interpreted in view of H1 and H2 hypotheses within the LR framework. The performance of the models, controlled by the levels of incorrect responses and the empirical cross entropy, demonstrated that the proposed LR models are successful in verifying the authenticity of the wolframite samples.
Geochemical wolframite fingerprinting
中文翻译:

地球化学黑钨矿指纹图谱–激光烧蚀ICP-MS数据的似然比方法
美国政府法案已将黑钨矿指定为“冲突矿物”,该法案要求使用这些矿物的公司必须报告其来源。来自刚果民主共和国冲突地区的矿物应排除在市场之外,因为它们的非法采矿,贸易和税收被认为会助长正在进行的暴力冲突。德国联邦地球科学与自然资源研究所(BGR)基于激光烧蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法开发了一种用于钨铁矿的地球化学指纹图谱方法。测定了来自64个矿山的约5300个黑钨矿晶粒中的46种元素的浓度。通过考虑两个相反的假设,可以将验证黑钨矿样品的声明来源确认为法医问题。1),这两个样本分别来自不同的矿山(H 2)。该解决方案是使用似然比(LR)理论找到的。由于多维性,每个样本内缺乏正态分布的数据以及样本内的离散程度相对于样本之间的离散程度巨大,因此必须对经典的LR模型进行修改。稳健的主成分分析和线性判别分析用于表征样品。两个样本的相似性由Kolmogorov-Smirnov距离表示,这些距离是根据H 1和H 2来解释的LR框架内的假设。该模型的性能受错误响应的水平和经验交叉熵的控制,表明所提出的LR模型成功地验证了黑钨矿样品的真实性。

地球化学黑钨矿指纹图谱











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号