Nano Research ( IF 9.5 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-14 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-018-2045-5 Antonio J. Martínez-Galera , José M. Gómez-Rodríguez
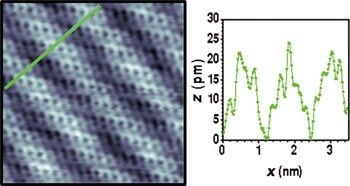
Predicting the properties of two-dimensional (2D) materials as graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) monolayers after their growth on any given substrate is a major challenge. While the influence of the electron configuration of the atoms of the underlying surface is well-understood, the effect of substrate geometry still remains unclear. The structural properties of h-BN monolayers grown on a rectangularly packed Rh(110) surface were characterized in situ by ultrahigh vacuum scanning tunneling microscopy and were compared to those that this material exhibits when grown on substrates showing different crystallographic orientations. Although the h-BN monolayer grown on Rh(110) was dominated by a unique quasiunidimensional moiré pattern, suggesting considerable interface interaction, the moiré corrugation was unexpectedly smaller than those reported for strongly interacting interfaces with hexagonal-terminated substrates, owing to differences in the possible binding landscapes at interfaces with differently oriented substrates. Moreover, a rule was derived for predicting how interface corrugation and the existence and extent of subregions within moiré supercells containing favorable sites for orbital mixing between h-BN monolayers and their supports depend on substrate symmetry. These general symmetry considerations can be applied to numerous 2D materials, including graphene, thereby enabling the prediction of how substrate choice determines the properties of these materials. Furthermore, they could also provide new routes for tuning 2D material properties and for developing nanotemplates showing different geometries for growing adsorbate superlattices.
中文翻译:

金属载体面内对称性对六方氮化硼和石墨烯单层波纹的影响
预测二维(2D)材料在任何给定基材上生长后作为石墨烯和六方氮化硼(h-BN)单层的性能是一项重大挑战。尽管下面的表面的原子的电子构型的影响是众所周知的,但是衬底几何形状的影响仍然不清楚。原位表征在矩形堆积的Rh(110)表面上生长的h-BN单层的结构特性通过超高真空扫描隧道显微镜进行了比较,并与该材料在具有不同晶体学取向的基板上生长时所展现的材料进行了比较。尽管在Rh(110)上生长的h-BN单层被独特的准一维莫尔条纹所占据,这表明大量的界面相互作用,但是由于波纹的差异,莫尔波纹意外地小于与六边形终止的底物发生强相互作用的界面所报道的波纹。与取向不同的基材的界面处可能存在的结合景观。此外,推导了一个规则,用于预测界面波纹以及在莫尔超级细胞中包含h-BN单层与其支撑物之间的轨道混合的有利位点的波纹区域中子区域的存在和程度如何取决于底物的对称性。这些一般的对称性考虑因素可以应用于包括石墨烯在内的多种2D材料,从而能够预测基材选择如何确定这些材料的特性。此外,它们还可以提供新的途径来调整2D材料的性能,以及开发显示出不同几何形状的纳米模板以生长吸附剂超晶格。












































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号