Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-13 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1947-5 Michael J. Van Stipdonk 1 , Anna Iacovino 1 , Irena Tatosian 1
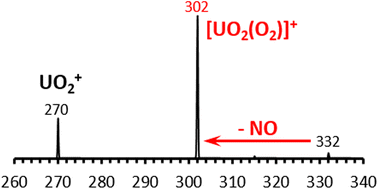
Developing a comprehensive understanding of the reactivity of uranium-containing species remains an important goal in areas ranging from the development of nuclear fuel processing methods to studies of the migration and fate of the element in the environment. Electrospray ionization (ESI) is an effective way to generate gas-phase complexes containing uranium for subsequent studies of intrinsic structure and reactivity. Recent experiments by our group have demonstrated that the relatively low levels of residual H2O in a 2-D, linear ion trap (LIT) make it possible to examine fragmentation pathways and reactions not observed in earlier studies conducted with 3-D ion traps (Van Stipdonk et al. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 14, 1205–1214, 2003). In the present study, we revisited the dissociation of complexes composed of uranyl nitrate cation [UVIO2(NO3)]+ coordinated by alcohol ligands (methanol and ethanol) using the 2-D LIT. With relatively low levels of background H2O, collision-induced dissociation (CID) of [UVIO2(NO3)]+ primarily creates [UO2(O2)]+ by the ejection of NO. However, CID (using He as collision gas) of [UVIO2(NO3)]+ creates [UO2(H2O)]+ and UO2+ when the 2-D LIT is used with higher levels of background H2O. Based on the results presented here, we propose that product ion spectrum in the previous experiments was the result of a two-step process: initial formation of [UVIO2(O2)]+ followed by rapid exchange of O2 for H2O by ion-molecule reaction. Our experiments illustrate the impact of residual H2O in ion trap instruments on the product ions generated by CID and provide a more accurate description of the intrinsic dissociation pathway for [UVIO2(NO3)]+.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

背景H的影响
从开发核燃料处理方法到研究环境中元素的迁移和归宿等领域,全面理解含铀物种的反应性仍然是一个重要目标。电喷雾电离(ESI)是产生含铀的气相络合物的有效方法,可用于后续的固有结构和反应性研究。我们小组最近的实验表明,二维线性离子阱(LIT)中残留H 2 O的含量相对较低,因此可以检查在早期使用3-D离子阱进行的研究中未观察到的裂解途径和反应(范Stipdonk等人J. PM。SOC。质谱Spectrom。14,1205至14年,2003)。在本研究中,我们使用2-LIT重新研究了由硝酸铀酰阳离子[U VI O 2(NO 3)] +与醇配体(甲醇和乙醇)配位的复合物的解离。在背景H 2 O含量相对较低的情况下,[U VI O 2(NO 3)] +的碰撞诱导解离(CID)主要是通过NO的喷射产生[UO 2(O 2)] +。但是,[U VI O 2(NO 3)] +的CID(使用He作为碰撞气体)会生成[UO 2(H 2 O)] +和UO 2 +当将2-D LIT与较高水平的背景H 2 O一起使用时。根据此处显示的结果,我们建议先前实验中的产物离子谱是两个步骤的过程:初步形成[C VI ø 2(O 2)] +,其次是O的快速交换2用于h 2 ö通过离子-分子反应。我们的实验说明了离子阱仪器中残留的H 2 O对CID生成的产物离子的影响,并为[U VI]的内在解离途径提供了更准确的描述。O 2(NO 3)] +。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号