Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-12 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1931-0 Shuang Yang 1 , Wells W. Wu 2 , Rong-Fong Shen 2 , Marshall Bern 3 , John Cipollo 4
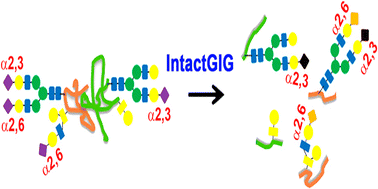
Mass spectrometric analysis of intact glycopeptides can reveal detailed information about glycosite, glycan structural features, and their heterogeneity. Sialyl glycopeptides can be positively, negatively, or neutrally charged depending on pH of their buffer solution and ionization conditions. To detect sialoglycopeptides, a negative-ion mode mass spectrometry may be applied with a minimal loss of sialic acids, although the positively charged or neutral glycopeptides may be excluded. Alternatively, the sialyl glycopeptides can be identified using positive-ion mode analysis by doping a high concentration of sodium salts to the analytes. Although manipulation of unmodified sialoglycopeptides can be useful for analysis of samples, less than optimal ionization, facile loss of sialyl and unfavorable ionization of accompanying non-sialyl peptides make such strategies suboptimal. Currently available chemical derivatization methods, while stabilizing for sialic acid, mask sialic acid linkage configuration. Here, we report the development of a novel approach to neutralize sialic acids via sequentially chemical modification that also reveals their linkage configuration, often an important determinant in biological function. This method utilizes several components to facilitate glycopeptide identification. These include the following: solid phase derivatization, enhanced ionization of sialoglycopeptides, differentiation of sialic acid linkage, and enrichment of the modified glycopeptides by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. This technology can be used as a tool for quantitative analysis of protein sialylation in diseases with determination of sialic acid linkage configuration.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用IntactGIG-HILIC通过差异化学修饰鉴定完整糖肽上的唾液酸键
完整糖肽的质谱分析可以揭示有关糖位,聚糖结构特征及其异质性的详细信息。唾液酸糖肽可以带正电荷,带负电荷或中性电荷,具体取决于其缓冲溶液的pH值和电离条件。为了检测唾液酸糖肽,可以应用负离子模式质谱分析法以最小程度的唾液酸损失,尽管可以排除带正电或中性的糖肽。或者,可以通过将高浓度的钠盐掺入分析物来使用正离子模式分析来鉴定唾液酸糖肽。尽管未修饰的唾液酸多肽的处理可用于样品分析,但远不及最佳电离,唾液酸基的容易损失和伴随的非唾液酸基肽的不利的电离使得这种策略不是最佳的。当前可用的化学衍生化方法,同时稳定用于唾液酸,掩盖唾液酸的键合构型。在这里,我们报告了一种通过顺序化学修饰来中和唾液酸的新方法的开发,该方法还揭示了它们的连接构型,通常是生物学功能中的重要决定因素。该方法利用了几种成分来促进糖肽的鉴定。这些包括:固相衍生化,唾液酸多肽的离子化增强,唾液酸键的分化以及通过亲水相互作用液相色谱法富集修饰的糖肽。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号