Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-03-19 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0982-1 David L. Duewer , Margaret C. Kline , Erica L. Romsos , Blaza Toman
The highly multiplexed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays used for forensic human identification perform best when used with an accurately determined quantity of input DNA. To help ensure the reliable performance of these assays, we are developing a certified reference material (CRM) for calibrating human genomic DNA working standards. To enable sharing information over time and place, CRMs must provide accurate and stable values that are metrologically traceable to a common reference. We have shown that droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) limiting dilution end-point measurements of the concentration of DNA copies per volume of sample can be traceably linked to the International System of Units (SI). Unlike values assigned using conventional relationships between ultraviolet absorbance and DNA mass concentration, entity-based ddPCR measurements are expected to be stable over time. However, the forensic community expects DNA quantity to be stated in terms of mass concentration rather than entity concentration. The transformation can be accomplished given SI-traceable values and uncertainties for the number of nucleotide bases per human haploid genome equivalent (HHGE) and the average molar mass of a nucleotide monomer in the DNA polymer. This report presents the considerations required to establish the metrological traceability of ddPCR-based mass concentration estimates of human nuclear DNA.
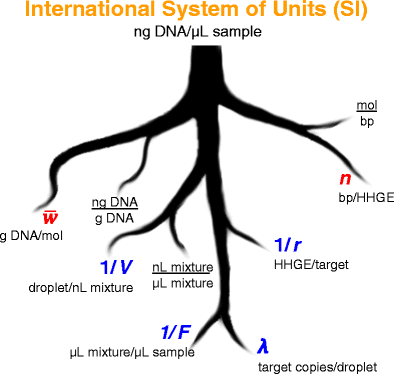
The roots of metrological traceability for human nuclear DNA mass concentration results. Values for the factors in blue must be established experimentally. Values for the factors in red have been established from authoritative source materials. HHGE stands for “haploid human genome equivalent”; there are two HHGE per diploid human genome.
中文翻译:

评估液滴数字PCR以定量人类基因组DNA:将每纳升的拷贝数转换为每微升纳克的核DNA
当与准确确定数量的输入DNA一起使用时,用于法医鉴定的高度多重聚合酶链反应(PCR)分析效果最佳。为了帮助确保这些测定的可靠性能,我们正在开发用于校准人类基因组DNA工作标准的认证参考材料(CRM)。为了能够随时间和地点共享信息,CRM必须提供准确且稳定的值,这些值可通过计量学溯源到通用参考。我们已经表明,液滴数字PCR(ddPCR)限制了每份样品中DNA拷贝浓度的稀释终点稀释测量,可以追溯到国际单位制(SI)。与使用紫外线吸收率和DNA质量浓度之间的常规关系指定的值不同,基于实体的ddPCR测量值预计会随着时间的推移而保持稳定。但是,法医界期望DNA数量以质量浓度而不是实体浓度来表示。给定每个人单倍体基因组当量(HHGE)的核苷酸碱基数和DNA聚合物中核苷酸单体的平均摩尔质量的SI可追踪值和不确定性,就可以完成转化。本报告提出了建立基于ddPCR的人类核DNA质量浓度估计值的计量可追溯性所需的考虑因素。给定每个人单倍体基因组当量(HHGE)的核苷酸碱基数和DNA聚合物中核苷酸单体的平均摩尔质量的SI可追踪值和不确定性,就可以完成转化。本报告提出了建立基于ddPCR的人类核DNA质量浓度估计值的计量可追溯性所需的考虑因素。给定每个人单倍体基因组当量(HHGE)的核苷酸碱基数和DNA聚合物中核苷酸单体的平均摩尔质量的SI可追踪值和不确定性,就可以完成转化。本报告提出了建立基于ddPCR的人类核DNA质量浓度估算值的计量可追溯性所需的考虑因素。

得出人类核DNA质量浓度的计量可追溯性根源。蓝色中的因子值必须通过实验确定。红色的值已从权威原始资料中确定。HHGE代表“单倍体人类基因组等效物”;每个二倍体人类基因组有两个HHGE。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号