Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-03-24 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1010-1 Tigst Demeke , David Dobnik
The number of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) on the market is steadily increasing. Because of regulation of cultivation and trade of GMOs in several countries, there is pressure for their accurate detection and quantification. Today, DNA-based approaches are more popular for this purpose than protein-based methods, and real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) is still the gold standard in GMO analytics. However, digital PCR (dPCR) offers several advantages over qPCR, making this new technique appealing also for GMO analysis. This critical review focuses on the use of dPCR for the purpose of GMO quantification and addresses parameters which are important for achieving accurate and reliable results, such as the quality and purity of DNA and reaction optimization. Three critical factors are explored and discussed in more depth: correct classification of partitions as positive, correctly determined partition volume, and dilution factor. This review could serve as a guide for all laboratories implementing dPCR. Most of the parameters discussed are applicable to fields other than purely GMO testing.
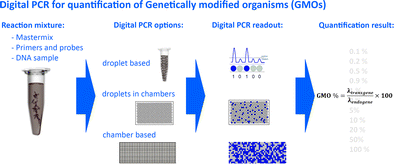
There are generally three different options for absolute quantification of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) using digital PCR: droplet- or chamber-based and droplets in chambers. All have in common the distribution of reaction mixture into several partitions, which are all subjected to PCR and scored at the end-point as positive or negative. Based on these results GMO content can be calculated.
中文翻译:

用于检测和定量转基因生物的数字PCR的关键评估
市场上的转基因生物(GMOs)的数量正在稳步增加。由于一些国家对转基因生物的种植和贸易进行了监管,因此对其进行准确检测和定量存在压力。如今,基于DNA的方法比基于蛋白质的方法更受欢迎,并且实时定量PCR(qPCR)仍然是GMO分析中的黄金标准。但是,数字PCR(dPCR)与qPCR相比具有许多优势,这使得这项新技术也对GMO分析具有吸引力。这篇重要的评论集中在dPCR在GMO定量分析中的用途,并讨论了对于获得准确可靠的结果至关重要的参数,例如DNA的质量和纯度以及反应优化。对三个关键因素进行了更深入的探讨和讨论:将分区正确分类为阳性,正确确定分区体积和稀释倍数。这项审查可以作为所有实施dPCR的实验室的指南。讨论的大多数参数都适用于纯GMO测试以外的领域。

对于使用数字PCR对转基因生物(GMO)进行绝对定量,通常存在三种不同的选择:基于液滴或基于小室的小滴以及基于小室的小滴。所有这些都具有将反应混合物分配到几个分区中的共同点,这些分区都经过PCR并在终点处记为阳性或阴性。基于这些结果,可以计算出GMO含量。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号