Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-03-16 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1928-8 Shelley N. Jackson 1 , Ludovic Muller 1 , Aurelie Roux 1 , Berk Oktem 2 , Eugene Moskovets 2 , Vladimir M. Doroshenko 2 , Amina S. Woods 1
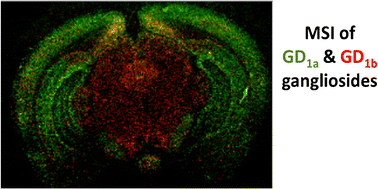
Matrix-assisted laser/desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) is widely used as a unique tool to record the distribution of a large range of biomolecules in tissues. 2,6-Dihydroxyacetophenone (DHA) matrix has been shown to provide efficient ionization of lipids, especially gangliosides. The major drawback for DHA as it applies to MS imaging is that it sublimes under vacuum (low pressure) at the extended time necessary to complete both high spatial and mass resolution MSI studies of whole organs. To overcome the problem of sublimation, we used an atmospheric pressure (AP)-MALDI source to obtain high spatial resolution images of lipids in the brain using a high mass resolution mass spectrometer. Additionally, the advantages of atmospheric pressure and DHA for imaging gangliosides are highlighted. The imaging of [M–H]− and [M–H2O–H]− mass peaks for GD1 gangliosides showed different distribution, most likely reflecting the different spatial distribution of GD1a and GD1b species in the brain.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用2,6-二羟基苯乙酮的神经节苷脂的AP-MALDI质谱成像
基质辅助激光/解吸电离(MALDI)质谱成像(MSI)被广泛用作记录组织中大范围生物分子分布的独特工具。2,6-二羟基苯乙酮(DHA)基质已被证明可有效地脂类电离,尤其是神经节苷脂。DHA应用于MS成像的主要缺点是,它在真空(低压)下会在完成整个器官的高空间分辨率和质量分辨率MSI研究所需的延长时间内升华。为了克服升华问题,我们使用大气压(AP)-MALDI源使用高分辨率质谱仪获得了大脑中脂质的高空间分辨率图像。此外,突出显示了大气压和DHA对神经节苷脂成像的优势。[MH]的成像GD 1神经节苷脂的-和[M–H 2 O–H] -质量峰显示出不同的分布,最有可能反映了GD 1a和GD 1b在大脑中的空间分布不同。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号