Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-30 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0855-7 Jessica K. Román , Callee M. Walsh , Junho Oh , Catherine E. Dana , Sungmin Hong , Kyoo D. Jo , Marianne Alleyne , Nenad Miljkovic , Donald M. Cropek
Laser-ablation electrospray ionization (LAESI) imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) is an emerging bioanalytical tool for direct imaging and analysis of biological tissues. Performing ionization in an ambient environment, this technique requires little sample preparation and no additional matrix, and can be performed on natural, uneven surfaces. When combined with optical microscopy, the investigation of biological samples by LAESI allows for spatially resolved compositional analysis. We demonstrate here the applicability of LAESI-IMS for the chemical analysis of thin, desiccated biological samples, specifically Neotibicen pruinosus cicada wings. Positive-ion LAESI-IMS accurate ion-map data was acquired from several wing cells and superimposed onto optical images allowing for compositional comparisons across areas of the wing. Various putative chemical identifications were made indicating the presence of hydrocarbons, lipids/esters, amines/amides, and sulfonated/phosphorylated compounds. With the spatial resolution capability, surprising chemical distribution patterns were observed across the cicada wing, which may assist in correlating trends in surface properties with chemical distribution. Observed ions were either (1) equally dispersed across the wing, (2) more concentrated closer to the body of the insect (proximal end), or (3) more concentrated toward the tip of the wing (distal end). These findings demonstrate LAESI-IMS as a tool for the acquisition of spatially resolved chemical information from fragile, dried insect wings. This LAESI-IMS technique has important implications for the study of functional biomaterials, where understanding the correlation between chemical composition, physical structure, and biological function is critical.
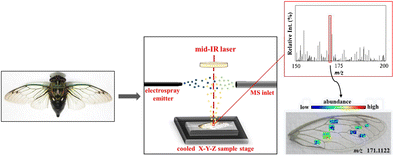
Positive-ion laser-ablation electrospray ionization mass spectrometry coupled with optical imaging provides a powerful tool for the spatially resolved chemical analysis of cicada wings
中文翻译:

使用激光消融电喷雾电离(LAESI)成像质谱(IMS)对蝉翼进行空间分辨化学分析
激光消融电喷雾电离(LAESI)成像质谱(IMS)是一种新兴的生物分析工具,用于对生物组织进行直接成像和分析。在周围环境中进行电离时,该技术几乎不需要样品制备,也不需要其他基质,并且可以在自然,不平坦的表面上进行。当与光学显微镜结合使用时,通过LAESI对生物样品进行研究可以进行空间分辨的成分分析。我们在这里证明了LAESI-IMS在薄的,干燥的生物样品,特别是新titibicen pruinosus的化学分析中的适用性。蝉的翅膀。正离子LAESI-IMS准确的离子图数据是从几个机翼电池中获取的,并叠加在光学图像上,从而可以跨机翼区域进行成分比较。进行了各种假定的化学鉴定,表明存在碳氢化合物,脂质/酯,胺/酰胺和磺化/磷酸化的化合物。利用空间分辨能力,在蝉翼上观察到了令人惊讶的化学分布模式,这可能有助于将表面特性趋势与化学分布相关联。观察到的离子要么(1)均匀分布在机翼上,要么(2)更加靠近昆虫的身体(近端)集中,或者(3)朝向机翼的尖端(远端)集中。这些发现表明,LAESI-IMS是一种用于从脆弱,干燥的昆虫翅膀中获取空间分辨的化学信息的工具。这种LAESI-IMS技术对功能性生物材料的研究具有重要意义,在这种情况下,了解化学成分,物理结构和生物学功能之间的相关性至关重要。

正离子激光烧蚀电喷雾电离质谱结合光学成像为蝉翼的空间分辨化学分析提供了强大的工具










































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号