Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-30 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0857-5 Meng Hu , Erik Müller , Emma L. Schymanski , Christoph Ruttkies , Tobias Schulze , Werner Brack , Martin Krauss
In nontarget screening, structure elucidation of small molecules from high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) data is challenging, particularly the selection of the most likely candidate structure among the many retrieved from compound databases. Several fragmentation and retention prediction methods have been developed to improve this candidate selection. In order to evaluate their performance, we compared two in silico fragmenters (MetFrag and CFM-ID) and two retention time prediction models (based on the chromatographic hydrophobicity index (CHI) and on log D). A set of 78 known organic micropollutants was analyzed by liquid chromatography coupled to a LTQ Orbitrap HRMS with electrospray ionization (ESI) in positive and negative mode using two fragmentation techniques with different collision energies. Both fragmenters (MetFrag and CFM-ID) performed well for most compounds, with average ranking the correct candidate structure within the top 25% and 22 to 37% for ESI+ and ESI− mode, respectively. The rank of the correct candidate structure slightly improved when MetFrag and CFM-ID were combined. For unknown compounds detected in both ESI+ and ESI−, generally positive mode mass spectra were better for further structure elucidation. Both retention prediction models performed reasonably well for more hydrophobic compounds but not for early eluting hydrophilic substances. The log D prediction showed a better accuracy than the CHI model. Although the two fragmentation prediction methods are more diagnostic and sensitive for candidate selection, the inclusion of retention prediction by calculating a consensus score with optimized weighting can improve the ranking of correct candidates as compared to the individual methods.
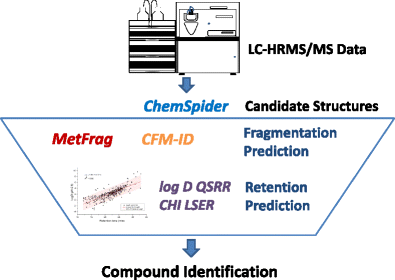
Consensus workflow for combining fragmentation and retention prediction in LC-HRMS-based micropollutant identification
中文翻译:

结合碎裂和保留预测的LC-HRMS鉴别有机微污染物的性能
在非目标筛选中,从高分辨率质谱(HRMS)数据阐明小分子的结构具有挑战性,尤其是在从化合物数据库中检索到的最可能的候选结构中进行选择。已经开发了几种碎片化和保留预测方法来改善该候选物的选择。为了评估其性能,我们比较了两个计算机片段化器(MetFrag和CFM-ID)和两个保留时间预测模型(基于色谱疏水性指数(CHI)和log D)。使用两种具有不同碰撞能量的裂解技术,通过液相色谱与带有电喷雾电离(ESI)的LTQ Orbitrap HRMS液相色谱联用,分析了78种已知的有机微污染物。两种片段化剂(MetFrag和CFM-ID)在大多数化合物中均表现良好,对于ESI +和ESI-模式,平均在正确的候选结构中位居前25%和22至37%之内。当MetFrag和CFM-ID结合使用时,正确候选结构的等级稍有提高。对于在ESI +和ESI-中都检测到的未知化合物,通常正模式质谱更好地用于进一步的结构阐明。两种保留预测模型对于疏水性较高的化合物均表现良好,但对于较早洗脱的亲水性物质却没有。日志D预测显示出比CHI模型更好的准确性。尽管这两种碎片预测方法对候选物的选择更具诊断性和敏感性,但与单个方法相比,通过计算具有优化权重的共识分数来包含保留预测可以改善正确候选物的排名。

在基于LC-HRMS的微污染物识别中结合碎片和保留预测的共识性工作流程











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号