Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-02-14 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0850-z Tingting Bai , Meng Wang , Min Cao , Juan Zhang , Kangzhen Zhang , Ping Zhou , Zhengxia Liu , Ying Liu , Zhirui Guo , Xiang Lu
Lateral flow assay strips (LFASs) with Au nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely used as a probe for biomarkers in point-of-care testing; however, there still remain challenges in detection sensitivity and quantitative analysis. In this study, we developed a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based LFAS for quantitative analysis of a biomarker in the low concentration range. Moreover, apart from conventional Au NPs, three other types of citrate-capped Au-Ag bimetallic NPs: Au core with Ag shell NPs (Au@Ag NPs), rattle-like Au core in Ag-Au shell NPs (Au@Ag-Au NPs) and Ag-Au NPs were prepared and functionalized, and their solution-based SERS activities were comprehensively studied by experimental measurement and theoretical analysis. The results clearly indicated that the citrate-capped Au@Ag-Au NPs exhibited the highest SERS activity among the probes tested. Au@Ag-Au NPs were used as both optical and SERS probes in a SERS-based LFAS. In the presence of the analyte at high concentrations, a purple color appeared in the test zone. Highly sensitive and quantitative analysis was realized by measurement of SERS signals from the test lines. One of the most specific markers for cardiac injury, cardiac troponin I (cTnI), was chosen as the detection model. The detection limit of the SERS-based LFAS for cardiac troponin I was 0.09 ng/mL, lowered by nearly 50 times compared with visual results, and could be further lowered by optimization. These results demonstrated that the SERS-based LFAS using citrate-capped Au@Ag-Au NPs as probes can be a powerful tool for highly sensitive and quantitative detection of biomarkers.
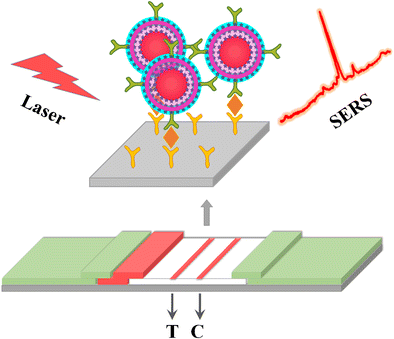
A surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based lateral flow assay strip using rattle-like Au core in Ag-Au shell (Au@Ag-Au) nanoparticles as probes was developed for quantitative analysis of a biomarker, with a detection limit nearly 50 times lower than that of visual assessment. C control line, T test line
中文翻译:

功能化的Au @ Ag-Au纳米粒子作为光学和SERS双探针用于侧向流传感
具有Au纳米颗粒(NPs)的侧向流动检测条(LFASs)已广泛用作即时检验中生物标志物的探针。然而,在检测灵敏度和定量分析方面仍然存在挑战。在这项研究中,我们开发了基于表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)的LFAS,用于在低浓度范围内对生物标志物进行定量分析。此外,除常规的金纳米颗粒外,还有三种其他类型的柠檬酸盐封端的金-银双金属纳米颗粒:带有Ag壳NP的Au核(Au @ Ag NPs),Ag-Au壳NP中的拨浪鼓状的Au核(Au @ Ag-制备并官能化了Au NPs和Ag-Au NPs,并通过实验测量和理论分析全面研究了它们基于溶液的SERS活性。结果清楚地表明,在所测试的探针中,柠檬酸盐封端的Au @ Ag-Au NPs表现出最高的SERS活性。在基于SERS的LFAS中,Au @ Ag-Au NP既用作光学探针又用作SERS探针。在存在高浓度分析物的情况下,测试区域会出现紫色。通过测量来自测试线的SERS信号实现了高度灵敏和定量的分析。心脏损伤最具体的标志之一,即肌钙蛋白I(cTnI)被选为检测模型。基于SERS的LFAS对心脏肌钙蛋白I的检出限为0.09 ng / mL,与视觉结果相比降低了近50倍,并且可以通过优化进一步降低。

开发了一种基于表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)的侧向流动检测条,其以Ag-Au壳(Au @ Ag-Au)纳米粒子中的拨浪鼓状Au芯为探针,用于生物标记物的定量分析,其检测极限接近比视觉评估低50倍。C控制线,T测试线











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号