Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-02-14 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0917-x Sherri B. Turnipseed , Joseph M. Storey , I-Lin Wu , Charles M. Gieseker , Nicholas R. Hasbrouck , Tina C. Crosby , Wendy C. Andersen , Shanae Lanier , Christine R. Casey , Robert Burger , Mark R. Madson
The ability to detect chemical contaminants, including veterinary drug residues in animal products such as fish, is an important example of food safety analysis. In this paper, a liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) screening method using a quadrupole-Orbitrap instrument was applied to the analysis of veterinary drug residues in incurred tissues from aquacultured channel catfish, rainbow trout, and Atlantic salmon and imported aquacultured products including European eel, yellow croaker, and tilapia. Compared to traditional MS methods, the use of HRMS with nontargeted data acquisition and exact mass measurement capability greatly increased the scope of compounds that could be monitored simultaneously. The fish samples were prepared for analysis using a simple efficient procedure that consisted of an acidic acetonitrile extraction followed by solid phase extraction cleanup. Two different HRMS acquisition programs were used to analyze the fish extracts. This method detected and identified veterinary drugs including quinolones, fluoroquinolones, avermectins, dyes, and aminopenicillins at residue levels in fish that had been dosed with those compounds. A metabolite of amoxicillin, amoxicillin diketone, was also found at high levels in catfish, trout, and salmon. The method was also used to characterize drug residues in imported fish. In addition to confirming findings of fluoroquinolone and sulfonamide residues that were found by traditional targeted MS methods, several new compounds including 2-amino mebendazole in eel and ofloxacin in croaker were detected and identified.
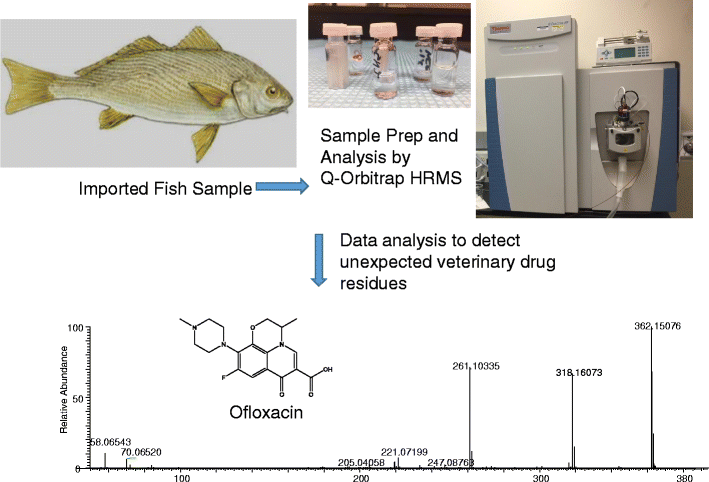
Aquacultured samples are analyzed with a high-resolution mass spectrometry screening method to detect and identify unusual veterinary drug residues including ofloxacin in an imported fish.
中文翻译:

高分辨率质谱筛查方法在鱼类和进口水产养殖样品中兽药残留中的应用和评估
检测化学污染物(包括鱼类等动物产品中的兽药残留)的能力是食品安全分析的重要示例。本文采用四极杆Orbitrap仪器进行液相色谱-高分辨率质谱(LC-HRMS)筛选方法,用于分析水产养殖channel鱼,虹鳟鱼和大西洋鲑和进口鲑鱼的组织中的兽药残留水产养殖产品,包括欧洲鳗鱼,黄花鱼和罗非鱼。与传统的质谱方法相比,将HRMS与非目标数据采集和精确的质量测量功能结合使用,大大增加了可以同时监测的化合物的范围。使用简单有效的程序准备鱼样品以进行分析,该程序包括酸性乙腈萃取,然后进行固相萃取净化。使用两种不同的HRMS采集程序来分析鱼的提取物。该方法以残留量检测并鉴定了已添加这些化合物的鱼类中的兽药,包括喹诺酮类,氟喹诺酮类,阿维菌素,染料和氨基青霉素。在cat鱼,鳟鱼和鲑鱼中也发现了阿莫西林的代谢产物阿莫西林二酮。该方法还用于表征进口鱼类中的药物残留。除了确认通过传统的靶向MS方法发现的氟喹诺酮和磺酰胺残基的发现外,

使用高分辨率质谱筛查方法对水产养殖样品进行分析,以检测和鉴定进口鱼中不常见的兽药残留,包括氧氟沙星。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号