Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-02-12 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0879-z Vahid Hamedpour , Geert J. Postma , Edwin van den Heuvel , Jeroen J. Jansen , Koji Suzuki , Daniel Citterio
This manuscript reports on the application of chemometric methods for the development of an optimized microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD). As an example, we applied chemometric methods for both device optimization and data processing of results of a colorimetric uric acid assay. Box–Behnken designs (BBD) were utilized for the optimization of the device geometry and the amount of thermal inkjet-deposited assay reagents, which affect the assay performance. Measurement outliers were detected in real time by partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) of scanned images. The colorimetric assay mechanism is based on the on-device formation of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) through the interaction of uric acid, ammonia, and poly(vinyl alcohol) with silver ions under mild basic conditions. The yellow color originating from visible light absorption by localized surface plasmon resonance of AgNPs can be detected by the naked eye or, more quantitatively, with a simple flat-bed scanner. Under optimized conditions, the linearity of the calibration curve ranges from 0.1–5 × 10−3 mol L−1 of uric acid with a limit of detection of 33.9 × 10−6 mol L−1 and a relative standard of deviation 4.5% (n = 3 for determination of 5.0 × 10−3 mol L−1 uric acid).
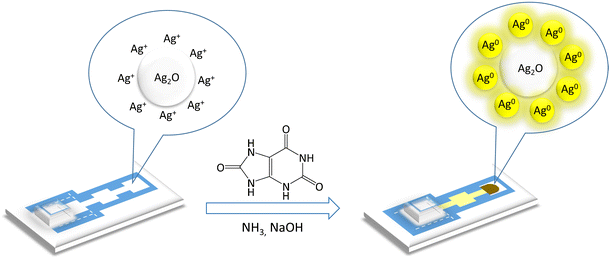
A chemometrics-assisted microfluidic paper-based analytical device was developed as a low-cost and rapid platform for the determination of uric acid (UA). The detection method is based on the chemical interaction of UA, ammonia, and polyvinyl alcohol under mild basic condition with silver ions inducing formation of yellow silver nanoparticles (AgNPs).
中文翻译:

化学计量学辅助的微流体纸基分析装置,用于银纳米粒子等离子体共振测定尿酸
该手稿报道了化学计量学方法在开发优化的基于纸的微流控分析设备(μPAD)方面的应用。例如,我们将化学计量学方法用于设备优化和比色尿酸测定结果的数据处理。Box–Behnken设计(BBD)用于优化设备的几何形状和热喷墨沉积的分析试剂的数量,这些会影响分析性能。通过扫描图像的偏最小二乘判别分析(PLS-DA)实时检测到测量异常值。比色测定机制是基于在温和的碱性条件下通过尿酸,氨水和聚乙烯醇与银离子的相互作用在装置上形成银纳米颗粒(AgNPs)。由AgNP的局部表面等离振子共振吸收可见光引起的黄色,可以用肉眼检测,或者用简单的平板扫描仪定量地检测。在优化条件下,校准曲线的线性范围为0.1–5×10-3 mol L -1的尿酸,检出限为33.9×10 -6 mol L -1,相对标准偏差为4.5%(n = 3,用于测定5.0×10 -3 mol L -1尿酸)。

开发了一种基于化学计量学的微流控纸基分析设备,作为测定尿酸(UA)的低成本,快速平台。该检测方法基于UA,氨和聚乙烯醇在温和的碱性条件下与银离子的化学相互作用,从而诱导黄色银纳米颗粒(AgNPs)的形成。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号