Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2018-02-06 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0863-7 Ganesh V Halade 1 , Anela Dorbane 2 , Kevin A Ingle 1 , Vasundhara Kain 1 , Jean-Marie Schmitter 2 , Boutayna Rhourri-Frih 2
Myocardial infarction (MI) and subsequent progressive heart failure pathology is the major cause of death worldwide; however, the mechanism of this pathology remains unclear. The present work aimed at testing the hypothesis whether the inflammatory response is superimposed with the formation of bioactive lipid resolving molecules at the site of the injured myocardium in acute heart failure pathology post-MI. In this view, we used a robust permanent coronary ligation model to induce MI, leading to decreased contractility index with marked wall thinning and necrosis of the infarcted left ventricle. Then, we applied mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) in positive and negative ionization modes to characterize the spatial distribution of left ventricle lipids in the infarcted myocardium post-MI. After micro-extraction, liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry was used to confirm the structures of the imaged lipids. Statistical tools such as principal component analysis were used to establish a comprehensive visualization of lipid profile changes in MI and no-MI hearts. Resolving bioactive molecules such as resolvin (Rv) D1, RvD5, RvE3, 17-HDHA, LXA4, and 18-HEPE were detected in negative ion mode MSI, whereas phosphatidyl cholines (PC) and oxidized derivatives thereof were detected in positive ion mode. MSI-based analysis demonstrated a significant increase in resolvin bioactive lipids with comprehensive lipid remodeling at the site of infarction. These results clearly indicate that infarcted myocardium is the primary location of inflammation-resolution pathomechanics which is critical for resolution of inflammation and heart failure pathophysiology.
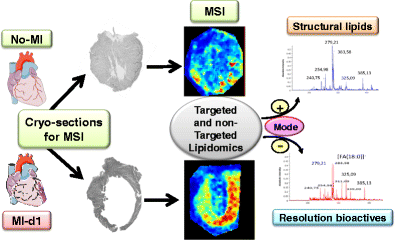
Applied scheme to determine comprehensive lipidomics in failing and non-failing heart.
中文翻译:

全面的有针对性和无针对性的脂质组学分析,可用于心脏衰竭和非衰竭的研究。
心肌梗塞(MI)和随后的进行性心力衰竭病理是全球范围内的主要死亡原因。然而,这种病理的机制仍不清楚。本研究旨在检验以下假设:在MI后急性心力衰竭病理中,炎症反应是否与受损心肌部位的生物活性脂质分解分子的形成相叠加。在这种观点下,我们使用了鲁棒的永久性冠状动脉结扎模型来诱发心肌梗死,从而导致收缩指数降低,并伴有明显的壁变薄和梗死的左心室坏死。然后,我们在正电离和负电离模式下应用质谱成像(MSI)来表征MI后梗死心肌中左心室脂质的空间分布。微萃取后 液相色谱-串联质谱联用用于确定成像脂质的结构。统计工具(例如主成分分析)用于建立MI和非MI心脏中脂质谱变化的全面可视化。解析生物活性分子,例如resolvin(Rv)D1,RvD5,RvE3、17-HDHA,LXA在负离子模式MSI中检测到图4和18-HEPE,而在正离子模式中检测到磷脂酰胆碱(PC)及其氧化衍生物。基于MSI的分析表明,在梗死部位,resolvin生物活性脂质显着增加,并且具有全面的脂质重塑。这些结果清楚地表明,梗塞的心肌是消炎机制的主要部位,这对消炎和心力衰竭的病理生理学至关重要。

确定失败和未失败心脏的综合脂质组学的应用方案。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号