Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-16 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-017-1871-0 Naruaki Imaoka 1 , Camille Houferak 2 , Megan P. Murphy 2 , Huong T. H. Nguyen 2 , Andy Dang 2 , František Tureček 2
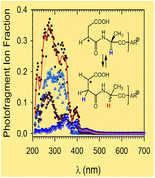
Peptide cation radicals of the z-type were produced by electron transfer dissociation (ETD) of peptide dications and studied by UV-Vis photodissociation (UVPD) action spectroscopy. Cation radicals containing the Asp (D), Asn (N), Glu (E), and Gln (Q) residues were found to spontaneously isomerize by hydrogen atom migrations upon ETD. Canonical N-terminal [z4 + H]+● fragment ion-radicals of the R-C●H-CONH- type, initially formed by N−Cα bond cleavage, were found to be minor components of the stable ion fraction. Vibronically broadened UV-Vis absorption spectra were calculated by time-dependent density functional theory for several [●DAAR + H]+ isomers and used to assign structures to the action spectra. The potential energy surface of [●DAAR + H]+ isomers was mapped by ab initio and density functional theory calculations that revealed multiple isomerization pathways by hydrogen atom migrations. The transition-state energies for the isomerizations were found to be lower than the dissociation thresholds, accounting for the isomerization in non-dissociating ions. The facile isomerization in [●XAAR + H]+ ions (X = D, N, E, and Q) was attributed to low-energy intermediates having the radical defect in the side chain that can promote hydrogen migration along backbone Cα positions. A similar side-chain mediated mechanism is suggested for the facile intermolecular hydrogen migration between the c- and [z + H]●-ETD fragments containing Asp, Asn, Glu, and Gln residues.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

紫外-可见光解离作用能谱揭示电子转移解离后肽阳离子自由基的自发异构化
Z型肽阳离子自由基是通过肽基离子的电子转移解离(ETD)产生的,并通过UV-Vis光解离(UVPD)作用光谱法进行研究。发现包含Asp(D),Asn(N),Glu(E)和Gln(Q)残基的阳离子自由基在ETD上通过氢原子迁移而自发异构化。发现最初由N- Cα键断裂形成的RC ● H-CONH-型的规范N末端[z 4 + H] +●碎片离子自由基是稳定离子部分的次要成分。通过时变密度泛函理论计算了几个[ ● DAAR + H] +异构体,用于将结构分配给作用谱。[势能面● DAAR + H] +的异构体是由从头和揭示的氢原子的迁移的多个异构化途径密度泛函理论计算映射。发现异构化的过渡态能量低于解离阈值,这说明了非解离离子的异构化。在容易异构化[ ● XAAR + H] +离子(X = d,N,E,和Q)归因于具有能够促进沿着骨干C氢气迁移侧链基团缺陷低能量的中间体α职位。对于包含Asp,Asn,Glu和Gln残基的c-和[z + H] ● -ETD片段之间的分子间氢迁移,建议采用类似的侧链介导机制。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号