Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-09 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-017-1863-0 Wei Wang 1, 2 , Steve Bajic 2 , Benzi John 1 , David R. Emerson 1
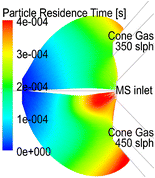
Understanding ion transport properties from the ion source to the mass spectrometer (MS) is essential for optimizing device performance. Numerical simulation helps in understanding of ion transport properties and, furthermore, facilitates instrument design. In contrast to previously reported numerical studies, ion transport simulations in a continuous injection mode whilst considering realistic space-charge effects have been carried out. The flow field was solved using Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equations, and a particle-in-cell (PIC) method was applied to solve a time-dependent electric field with local charge density. A series of ion transport simulations were carried out at different cone gas flow rates, ion source currents, and capillary voltages. A force evaluation analysis reveals that the electric force, the drag force, and the Brownian force are the three dominant forces acting on the ions. Both the experimental and simulation results indicate that cone gas flow rates of ≤250 slph (standard liter per hour) are important for high ion transmission efficiency, as higher cone gas flow rates reduce the ion signal significantly. The simulation results also show that the ion transmission efficiency reduces exponentially with an increased ion source current. Additionally, the ion loss due to space-charge effects has been found to be predominant at a higher ion source current, a lower capillary voltage, and a stronger cone gas counterflow. The interaction of the ion driving force, ion opposing force, and ion dispersion is discussed to illustrate ion transport mechanism in the ion source at atmospheric pressure.
Graphical Abstract
中文翻译:

大气压下纳米电喷雾离子源中离子迁移的数值模拟
了解从离子源到质谱仪(MS)的离子传输特性对于优化设备性能至关重要。数值模拟有助于理解离子传输特性,并且有助于仪器设计。与先前报道的数值研究相反,在考虑实际空间电荷效应的同时,进行了连续注入模式下的离子迁移模拟。使用雷诺平均的Navier-Stokes(RANS)方程求解流场,并应用单元格内粒子(PIC)方法求解局部电荷密度随时间变化的电场。在不同的锥形气体流速,离子源电流和毛细管电压下进行了一系列离子迁移模拟。力评估分析显示,电力,阻力,布朗力是作用在离子上的三个主导力。实验结果和模拟结果均表明,≤250slph(每小时标准升)的锥形气体流速对于提高离子传输效率非常重要,因为较高的锥形气体流速会大大降低离子信号。仿真结果还表明,离子传输效率随着离子源电流的增加而呈指数下降。另外,已经发现,由于空间电荷效应而导致的离子损失在较高的离子源电流,较低的毛细管电压和较强的锥气逆流情况下是主要的。讨论了离子驱动力,离子反作用力和离子弥散的相互作用,以说明在大气压下离子源中的离子传输机理。

图形概要









































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号