Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2017-12-29 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0811-y Jua Lee , Serenus Hua , Sung Hyeon Lee , Myung Jin Oh , Jaekyung Yun , Jin Young Kim , Jae-Han Kim , Jung Hoe Kim , Hyun Joo An
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide, largely because of difficulties in early diagnosis. Despite accumulating evidence indicating that aberrant glycosylation is associated with GC, site-specific localization of the glycosylation to increase specificity and sensitivity for clinical use is still an analytical challenge. Here, we created an analytical platform with a targeted glycoproteomic approach for GC biomarker discovery. Unlike the conventional glycomic approach with untargeted mass spectrometric profiling of released glycan, our platform is characterized by three key features: it is a target-protein-specific, glycosylation-site-specific, and structure-specific platform with a one-shot enzyme reaction. Serum haptoglobin enriched by immunoaffinity chromatography was subjected to multispecific proteolysis to generate site-specific glycopeptides and to investigate the macroheterogeneity and microheterogeneity. Glycopeptides were identified and quantified by nano liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and nano liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Ninety-six glycopeptides, each corresponding to a unique glycan/glycosite pairing, were tracked across all cancer and control samples. Differences in abundance between the two groups were marked by particularly high magnitudes. Three glycopeptides exhibited exceptionally high control-to-cancer fold changes along with receiver operating characteristic curve areas of 1.0, indicating perfect discrimination between the two groups. From the results taken together, our platform, which provides biological information as well as high sensitivity and reproducibility, may be useful for GC biomarker discovery.
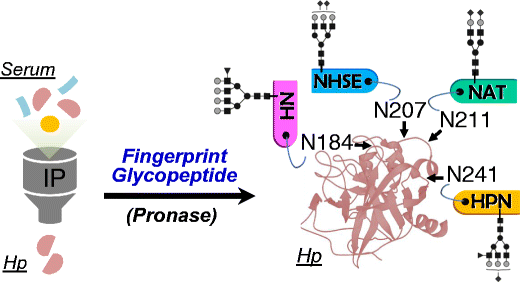
Graphical abstract
ᅟ
中文翻译:

用于血清触珠蛋白的靶向糖蛋白组学分析的指纹糖肽的指定:对胃癌生物标志物发现的见解
胃癌(GC)是全世界与癌症相关的死亡的主要原因之一,很大程度上是由于早期诊断的困难。尽管有越来越多的证据表明异常糖基化与GC有关,但糖基化的位点特异性定位以提高临床应用的特异性和敏感性仍然是一个分析难题。在这里,我们创建了具有针对性糖蛋白组学方法的分析平台,用于GC生物标志物的发现。与传统的具有释放的聚糖的非目标质谱分析的糖组学方法不同,我们的平台的特征在于三个关键特征:它是具有靶标蛋白质特异性,糖基化位点特异性和结构特异性的平台,具有一次酶促反应。通过免疫亲和层析富集的血清触珠蛋白进行多特异性蛋白水解以产生位点特异性糖肽,并研究大异质性和微异质性。通过纳米液相色谱-质谱法和纳米液相色谱-串联质谱法鉴定并定量糖肽。在所有癌症和对照样品中追踪了九十六个糖肽,每个肽对应于唯一的聚糖/糖基配对。两组之间的丰度差异特别明显。三种糖肽表现出异常高的癌旁控制倍数变化以及1.0的受体工作特征曲线区域,表明两组之间的完美区分。从综合的结果来看,我们的平台

图形概要
ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号