Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 3.8 ) Pub Date : 2017-12-26 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0810-z Jing Chen , Bosoon Park
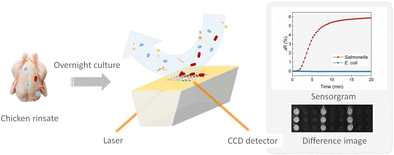
It is estimated that 95% of the foodborne infections are caused by 15 major pathogens. Therefore, rapid and effective multiplex screening techniques for these pathogens with improved efficiencies could benefit public health at lower costs. Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi) provides a label-free, multiplex analytical platform for pathogen screening. In this study, we have developed a singleplex immunoassay for Salmonella to evaluate the potential of SPRi in pathogen detection. Anti-Salmonella and control ligands were arrayed onto the SPRi sensor chip in a microarray format. The influences of ligand immobilization pH and concentration were optimized, and a pause flow protocol was adopted to improve assay rapidity and sensitivity. The method shows good specificity against 6 non-Salmonella species and was able to detect 5 of 6 Salmonella serotypes, including 3 serotypes most frequently associated with outbreaks. Limits of detection were found to be 2.1 × 106 CFU/mL in phosphate-buffered saline and 7.6 × 106 CFU/mL in the presence of chicken rinse matrix with 8.9 × 107 CFU/mL of indigenous microflora. The condition of antibody array regeneration was optimized for sequential sample injections. Finally, the SPRi immunoassay was used to detect Salmonella directly from artificially spiked chicken carcass rinse samples. As low as 6.8 CFU/mL of Salmonella could be detected after overnight enrichment in buffered peptone water, demonstrating the potential in streamlined pathogen screening with minimal sample preparation and without detection labels.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

食源性无标签筛查
据估计,95%的食源性感染是由15种主要病原体引起的。因此,针对这些病原体的快速有效的多重筛选技术具有更高的效率,可以以较低的成本使公众健康受益。表面等离振子共振成像(SPRi)为病原体筛查提供了无标记的多重分析平台。在这项研究中,我们开发了沙门氏菌的单重免疫测定法,以评估SPRi在病原体检测中的潜力。将抗沙门氏菌和对照配体以微阵列格式排列在SPRi传感器芯片上。优化了配体固定化pH和浓度的影响,并采用了暂停流动方案以提高测定的速度和灵敏度。该方法对6种非沙门氏菌种类,能够检测出6种沙门氏菌血清型中的5种,其中3种与暴发最频繁相关。 在磷酸盐缓冲液中的检出限为2.1×10 6 CFU / mL,在 有8.9×10 7 CFU / mL本地菌群的鸡漂洗基质存在下,检出限为7.6×10 6 CFU / mL 。抗体阵列再生的条件已针对顺序进样进行了优化。最后,使用SPRi免疫测定法直接从人工掺入的鸡car体冲洗样品中检测沙门氏菌。沙门氏菌低至6.8 CFU / mL 在缓冲蛋白ept水中浓缩过夜后即可检测到,可证明在最少的样品制备和没有检测标记的情况下,简化了病原体筛查的潜力。

ᅟ











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号