Nano Research ( IF 9.5 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-02 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-017-1928-1 Sen Lin , Peiling Xie , Mengmeng Luo , Qing Li , Ling Li , Jinzhao Zhang , Qinxiang Zheng , Hao Chen , Kaihui Nan
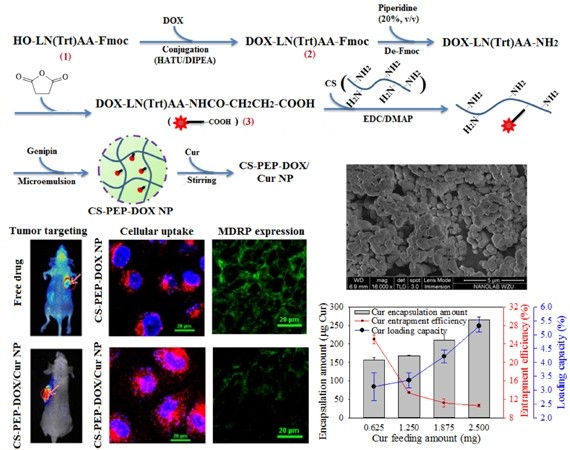
Multidrug resistance proteins (MDRPs), which are implicated in the mediation of multidrug resistance in tumors, represent the main obstacle to successful chemotherapy. As curcumin (Cur) exerts inhibitory effects on both the expression and function of MDRPs, a nanocarrier for the co-delivery of Cur and doxorubicin (DOX) was prepared to overcome MDR tumors through their synergistic effects. Owing to the overexpression of legumain in tumors, the release profile of DOX from this nanocarrier was designed to be legumain modulated, which was achieved by bridging DOX to a basic material (chitosan) with a legumain-sensitive peptide. Compared with nanoparticles that only contain DOX, the coadministration of DOX and Cur significantly inhibited multidrug resistance (P < 0.05) in a multidrug-resistant cancer cell model (MCF-7/ADR cell line), with cytotoxicity to normal cells (L929 cell line). Such inhibition could be ascribed to the increased DOX accumulation in the MCF-7/ADR nucleus. The co-delivery system exhibited good anticancer effects through prolonged circulation time, improved tumor-targeting efficiency, elevation of the tumor inhibition activity, and the suppression of MDRP expression. These data revealed the enormous potential of this co-delivery system for cancer therapy, especially in the later stages where multidrug resistance may develop.
中文翻译:

通过阿霉素和姜黄素与豆蔻因敏感的纳米载体共同给药有效抵抗多药耐药性
与肿瘤中的多药耐药性有关的多药耐药蛋白(MDRP)代表了成功化疗的主要障碍。由于姜黄素(Cur)对MDRPs的表达和功能均具有抑制作用,因此准备了用于共同递送Cur和阿霉素(DOX)的纳米载体,以通过其协同作用克服MDR肿瘤。由于肿瘤中豆科菌素的过表达,DOX从该纳米载体的释放曲线被设计为豆科菌素调节的,这是通过将DOX与豆科素敏感肽桥接到基本材料(壳聚糖)而实现的。与仅包含DOX的纳米颗粒相比,DOX和Cur的共同给药显着抑制了多药耐药性(P在多药耐药性癌细胞模型(MCF-7 / ADR细胞系)中具有<0.05),且对正常细胞(L929细胞系)具有细胞毒性。这种抑制作用可能归因于MCF-7 / ADR核中DOX积累的增加。共递送系统通过延长循环时间,提高的肿瘤靶向效率,提高的肿瘤抑制活性和抑制MDRP表达表现出良好的抗癌作用。这些数据揭示了这种共同给药系统在癌症治疗中的巨大潜力,尤其是在可能产生多药耐药性的后期阶段。











































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号