Nano Research ( IF 9.5 ) Pub Date : 2017-11-07 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-017-1878-7 Seong-Min Kim , Seyeong Lee , Dongyoon Kim , Dong-Hee Kang , Kisuk Yang , Seung-Woo Cho , Jin Seok Lee , Insung S. Choi , Kyungtae Kang , Myung-Han Yoon
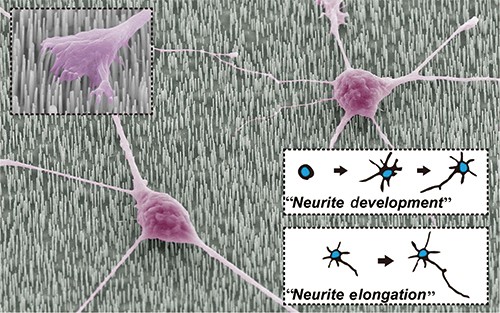
In this study, we report that height-controlled vertically etched silicon nano-column arrays (vSNAs) induce strong growth cone-to-substrate coupling and accelerate In vitroneurite development while preserving the essential features of initial neurite formation. Large-scale preparation of vSNAs with flat head morphology enabled the generation of well-controlled topographical stimulation without cellular impalement. A systematic analysis on topography-induced variations on cellular morphology and cytoskeletal dynamics was conducted. In addition, neurite development on the grid-patterned vSNAs exhibited preferential adhesion to the nanostructured region and outgrowth directionality. The arrangement of cytoskeletal proteins and the expression of a focal adhesion complex indicated that a strong coupling existed between the underlying nanocolumns and growth cones. Furthermore, the height-controlled nanocolumn substrates differentially modulated neurite polarization and elongation. Our findings provide an important insight into neuron-nanotopography interactions and their role in cell adhesion and neurite development.
中文翻译:

神经元生长锥与高度受控的垂直硅纳米柱的强接触耦合
在这项研究中,我们报告高度控制的垂直蚀刻的硅纳米柱阵列(vSNAs)诱导强烈的生长锥-底物耦合并加速体外神经突发育,同时保留初始神经突形成的基本特征。具有扁平头形态的vSNA的大规模制备能够产生不受细胞干扰的良好的地形刺激。对地形引起的细胞形态和细胞骨架动力学变化进行了系统分析。此外,在网格状vSNA上的神经突发育表现出对纳米结构区域的优先粘附和向外生长的方向性。细胞骨架蛋白的排列和粘着斑复合物的表达表明在下面的纳米柱和生长锥之间存在强耦合。此外,高度受控的纳米柱基质可不同地调节神经突的极化和伸长率。












































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号