Abstract
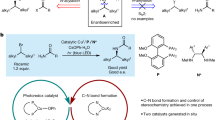
The development of enantiodivergent catalysts capable of preparing both enantiomeric products from one substrate in a controlled fashion is challenging. Introducing a switching function into the catalyst can address this challenge, allowing the chiral reaction environment to reversibly change during catalysis. Here we report a photoswitchable phosphate ligand, derived from 2,2′-biphenol, which axially coordinates as the counterion to an achiral manganese(III)-salen catalyst, providing the latter with the ability to switch stereoselectivity in the epoxidation of alkenes. The enantiomers of the chiral ligand exist as a pair of pseudo-enantiomers, which can be interconverted by irradiation with light of different wavelengths. The opposite axial chirality of these pseudo-enantiomers is efficiently transferred to the manganese(III)-salen catalyst. With this switchable supramolecular catalyst, the enantioselectivity of the epoxidation of a variety of alkenes can be controlled, resulting in opposite enantiomeric excesses of the epoxide products. This transfer of chirality from a photoswitchable anionic ligand to a metal complex broadens the scope of supramolecular catalysts.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are included in the paper and the Supplementary Information file. Any further relevant data are available from the corresponding authors on request. Crystallographic data for the structure Rac-Mn2 reported in this article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), under deposition number 2125340. Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/.
References
Bonner, W. A. Chirality and life. Origins Life Evol. Biosphere 25, 175–190 (1995).
Brady, D. & Jordaan, J. Advances in enzyme immobilisation. Biotechnol. Lett 31, 1639 (2009).
Vlatković, M., Collins, B. S. & Feringa, B. L. Dynamic responsive systems for catalytic function. Chem. Eur. J. 22, 17080–17111 (2016).
Dorel, R. & Feringa, B. L. Photoswitchable catalysis based on the isomerisation of double bonds. Chem. Commun. 55, 6477–6486 (2019).
Göstl, R., Senf, A. & Hecht, S. Remote-controlling chemical reactions by light: towards chemistry with high spatio-temporal resolution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 1982–1996 (2014).
Blanco, V., Leigh, D. A. & Marcos, V. Artificial switchable catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 5341–5370 (2015).
Koumura, N., Zijlstra, R. W., Van Delden, R. A., Harada, N. & Feringa, B. L. Light-driven monodirectional molecular rotor. Nature 401, 152–155 (1999).
García-López, V., Liu, D. & Tour, J. M. Light-activated organic molecular motors and their applications. Chem. Rev. 120, 79–124 (2020).
Koumura, N., Geertsema, E. M., Van Gelder, M. B., Meetsma, A. & Feringa, B. L. Second generation light-driven molecular motors. Unidirectional rotation controlled by a single stereogenic center with near-perfect photoequilibria and acceleration of the speed of rotation by structural modification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 5037–5051 (2002).
Pizzolato, S. F. et al. Central-to-helical-to-axial-to-central transfer of chirality with a photoresponsive catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 17278–17289 (2018).
Van Dijk, L. et al. Molecular machines for catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2, 0117 (2018).
Ihrig, S. P., Eisenreich, F. & Hecht, S. Photoswitchable polymerization catalysis: state of the art, challenges, and perspectives. Chem. Commun. 55, 4290–4298 (2019).
Romanazzi, G., Degennaro, L., Mastrorilli, P. & Luisi, R. Chiral switchable catalysts for dynamic control of enantioselectivity. ACS Catal. 7, 4100–4114 (2017).
Wang, J. & Feringa, B. L. Dynamic control of chiral space in a catalytic asymmetric reaction using a molecular motor. Science 331, 1429–1432 (2011).
Vlatković, M., Bernardi, L., Otten, E. & Feringa, B. L. Dual stereocontrol over the Henry reaction using a light- and heat-triggered organocatalyst. Chem. Commun. 50, 7773–7775 (2014).
Zhao, D., Neubauer, T. M. & Feringa, B. L. Dynamic control of chirality in phosphine ligands for enantioselective catalysis. Nat. Commun. 6, 6652 (2015).
Dorel, R. & Feringa, B. L. Stereodivergent anion binding catalysis with molecular motors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 785–789 (2020).
Dommaschk, M., Echavarren, J., Leigh, D. A., Marcos, V. & Singleton, T. A. Dynamic control of chiral space through local symmetry breaking in a rotaxane organocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 14955–14958 (2019).
Brak, K. & Jacobsen, E. N. Asymmetric ion-pairing catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 534–561 (2013).
Phipps, R. J., Hamilton, G. L. & Toste, F. D. The progression of chiral anions from concepts to applications in asymmetric catalysis. Nat. Chem. 4, 603–614 (2012).
Lacour, J., Monchaud, D. & Marsol, C. Effect of the medium on the oxaziridinium-catalyzed enantioselective epoxidation. Tetrahedron Lett. 43, 8257–8260 (2002).
Čorić, I. & List, B. Asymmetric spiroacetalization catalysed by confined Brønsted acids. Nature 483, 315–319 (2012).
LaLonde, R., Wang, Z., Mba, M., Lackner, A. & Toste, F. D. Gold(I)-catalyzed enantioselective synthesis of pyrazolidines, isoxazolidines, and tetrahydrooxazines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 598–601 (2010).
Mukherjee, S. & List, B. Chiral counteranions in asymmetric transition-metal catalysis: highly enantioselective Pd/Brønsted acid-catalyzed direct α-allylation of aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 11336–11337 (2007).
Li, C., Wang, C., Villa-Marcos, B. & Xiao, J. Chiral counteranion-aided asymmetric hydrogenation of acyclic imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 14450–14451 (2008).
Hennecke, U., Müller, C. H. & Fröhlich, R. Enantioselective haloetherification by asymmetric opening of meso-halonium ions. Org. Lett. 13, 860–863 (2011).
Liao, S. & List, B. Asymmetric counteranion-directed transition-metal catalysis: enantioselective epoxidation of alkenes with manganese(III) salen phosphate complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 628–631 (2010).
Merten, C., Pollok, C. H., Liao, S. & List, B. Stereochemical communication within a chiral ion pair catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 8841–8845 (2015).
Rutten, M. G. T. A., Vaandrager, F. W., Elemans, J. A. A. W. & Nolte, R. J. M. Encoding information into polymers. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2, 365–381 (2018).
Pizzolato, S. F., Štacko, P., Kistemaker, J. C., van Leeuwen, T. & Feringa, B. L. Phosphoramidite-based photoresponsive ligands displaying multifold transfer of chirality in dynamic enantioselective metal catalysis. Nat. Catal. 3, 488–496 (2020).
Feringa, B. L. The art of building small: from molecular switches to motors (Nobel lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 11060–11078 (2017).
Kistemaker, J. C., Pizzolato, S. F., van Leeuwen, T., Pijper, T. C. & Feringa, B. L. Spectroscopic and theoretical identification of two thermal isomerization pathways for bistable chiral overcrowded alkenes. Chem. Eur. J. 22, 13478–13487 (2016).
Zhang, W., Loebach, J. L., Wilson, S. R. & Jacobsen, E. N. Enantioselective epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins catalyzed by salen manganese complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 2801–2803 (1990).
Irie, R., Noda, K., Ito, Y., Matsumoto, N. & Katsuki, T. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins. Tetrahedron Lett. 31, 7345–7348 (1990).
Liao, S. & List, B. Asymmetric counteranion-directed iron catalysis: a highly enantioselective sulfoxidation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 354, 2363–2367 (2012).
McGarrigle, E. M. & Gilheany, D. G. Chromium- and manganese-salen promoted epoxidation of alkenes. Chem. Rev. 105, 1563–1602 (2005).
Vicario, J., Walko, M., Meetsma, A. & Feringa, B. L. Fine tuning of the rotary motion by structural modification in light-driven unidirectional molecular motors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 5127–5135 (2006).
Štacko, P. et al. Locked synchronous rotor motion in a molecular motor. Science 356, 964–968 (2017).
Skarżewski, J., Gupta, A. & Vogt, A. Influence of additional ligands on the two-phase epoxidation with sodium hypochlorite catalysed by (salen)manganese(III) complexes. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 103, L63–L68 (1995).
Jacobsen, E. N., Zhang, W., Muci, A. R., Ecker, J. R. & Deng, L. Highly enantioselective epoxidation catalysts derived from 1,2-diaminocyclohexane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 7063–7064 (1991).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the European Research Council (ERC Advanced Grant Number 74092 to R.J.M.N. and ERC Advanced Grant Number 227897 to B.L.F.) and by the Dutch Ministry of Education, Culture, and Science (Gravitation Programme 024.001.035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.J.M.N. conceived the project. P.J.G. and F.P.J.T.R. designed the synthesis of compound 1. P.J.G. carried out the synthesis of 1 and investigated the photochemical properties of compounds 1 and Mn2. X.C. performed the catalysis experiments and grew the crystals. P.T. determined and analysed the crystal structure. N.V. separated the enantiomers of 1 by chiral HPLC. B.L.F contributed with his knowledge on molecular photoswitches. R.J.M.N. and J.A.A.W.E. supervised the project. All authors discussed the results and helped write and discuss the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Synthesis thanks Zoraida Freixa and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary handling editor: Peter Seavill, in collaboration with the Nature Synthesis team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–90, Discussion and Tables 1–8.
Supplementary Data 1
Crystallographic data for Compound Rac-Mn2, CCDC 2125340.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 3
Unprocessed UV-vis and ECD data.
Source Data Fig. 4
Unprocessed 1H NMR data.
Source Data Fig. 6
Unprocessed chiral HPLC data.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Gilissen, P.J., Tinnemans, P. et al. Enantiodivergent epoxidation of alkenes with a photoswitchable phosphate manganese-salen complex. Nat. Synth 1, 873–882 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-022-00157-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44160-022-00157-7
This article is cited by
-
Design a new unsymmetrical Schiff base chiral Co-complex containing ionic liquid groups as a reusable green catalyst in the epoxidation of alkenes
Research on Chemical Intermediates (2024)